Platelet activating factor (PAF) is a potent pro-inflammatory lipid. We have shown that PAF is produced by the monolayer of cells underneath the retina (RPE cells) and we have data suggesting that oxidative stress increases the production of PAF-like compounds by the RPE. We have also shown that a RPE cells express PAF receptors. The agonist of such receptors can increase the production of VEGF by RPE cells, increase the migration of choroidal vascular endothelial cells in vitro, and increase choroidal vascular endothelial cell permeability. We are currently gathering data to determine the relevance of PAF in human AMD, with the goal of exploiting this molecule as a new therapeutic target for the disease.
Research Rational
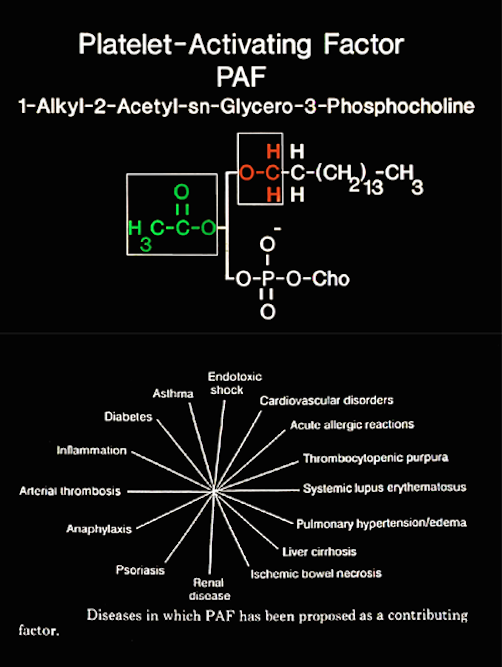
- Platelet-activating factor (PAF) is a potent pro-inflammatory lipid with diverse effects in many organ systems.
- The retina tissue is subject to high levels of irradiation with the generation of free radiclas.Photo-receptors of the outer segment membrane of the retina are extremely rich in polyunsaturated fatty acid esters in two positions of phosphatidylcholines, which can be rapidly oxidized.
- These oxidized products of phosphatidylcholines produce PAF and products with PAF-like activities.
- Significant evidence indicated PAF affects ocular inflammation and neovascularization.
Work in Progress
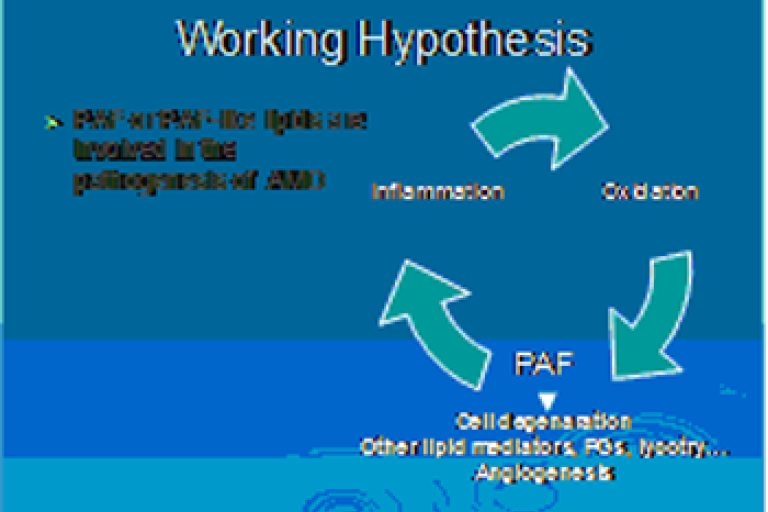
- The evidence of PAF involved in the development of AMD
- The role of PAF in oxidative damage of retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells.
- The mechanism of PAF participates in choroidal neovascularization (wet type AMD)
- The irregularities of systemic bioproducts of PAF in AMD subjects
- The potential therapeutic role of PAF receptor antagonist in the treatment of AMD
Research Tools
- Cultured RPE cells, ocular choroidal capillary endothelial cells
- Synthetic stable derivative PAF (cPAF) and antagonist of PAF-receptor
- Over 1000 serum samples from AMD patients and their age- and gender-matched controls
- High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and electrospray tandem mass epctrometry (LC-MS/MS)
Potential Collaboration
- Oxidation derivative measurement can be used to screen the oxidative damages of various agents in vitro or in vivo
- Serum sample from AMD subjects and controls can be used to screen other biomarkers in other age-related processes.