Research Focus
Our research focuses on elucidating the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying chronic liver
diseases. Key areas of investigation include:
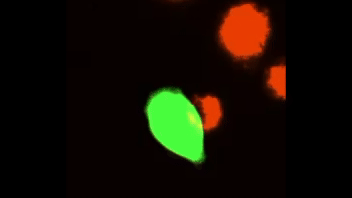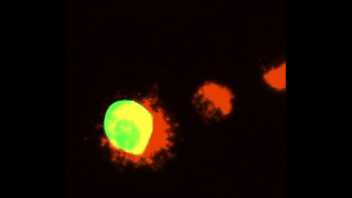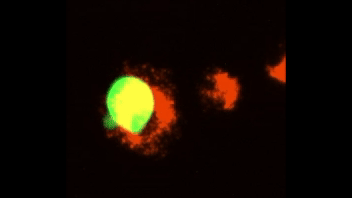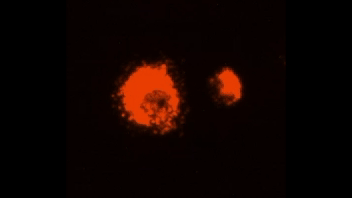
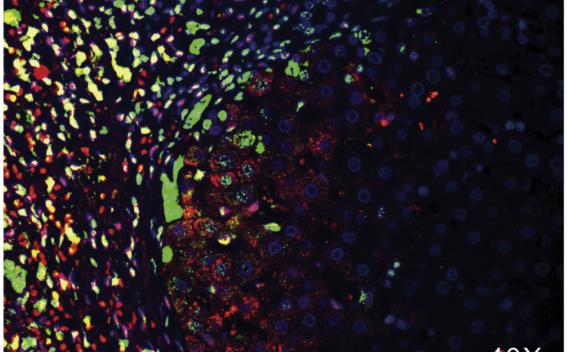
Efferocytosis of lipid-laden apoptotic hepatocytes (green) by BMDMs (red).
Inflammation in the Liver
We study how chronic inflammation is sustained in the liver and its role in the development of fibrosis and HCC. Recent discoveries include the identification of impaired macrophage efferocytosis as a crucial event in promoting chronic liver inflammation.
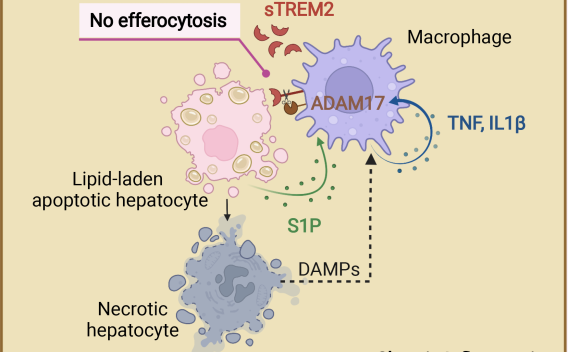
Role of Macrophages in Liver Diseases
Our work has highlighted the significance of macrophages in liver pathology, including their role in regulating liver inflammation, fibrosis, and tumorigenesis. We have identified NADPH oxidase 1 (NOX1) in liver macrophages as a key driver of HCC and demonstrated that macrophage autophagy prevents ASH development.
Innovative Therapeutic Targets
By characterizing novel molecular pathways and targets, such as TREM2 and CMPK2, we aim to develop innovative therapies for treating MASH, ASH, and HCC. Our research includes comprehensive investigations into the roles of these targets in liver disease progression and their potential as therapeutic interventions.

