At the Mitra Lab, we believe science can do wonders. Our mantra is ‘never-ever give up!’
Our Research
The Mitra lab is interested in studying glycogen metabolism related E3 ubiquitin ligases and their role in the pathogenesis of related neurological and neuromuscular diseases. To this end, we have characterized multiple glycogen metabolism related E3 ubiquitin ligases using novel mouse models and identified key mechanisms for their glycogen association. There are two simple questions we ask in our research:
- What is the mechanism by which the ubiquitination system affects glycogen metabolism?
- How do we develop the best therapeutics to fight glycogen metabolism related diseases?
Simply put, at the Mitra lab, we are actively working to identify novel cellular mechanisms of neurological and neuromuscular diseases where the ubiquitination system is perturbed and to develop the best therapeutic strategies for the same!
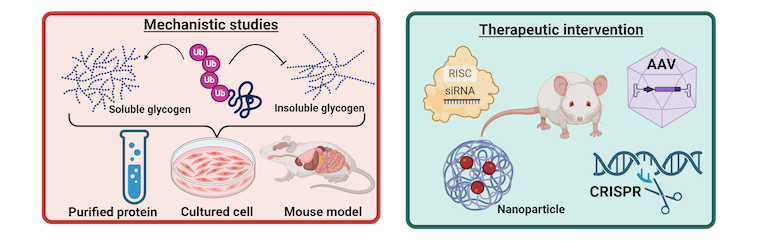
Role of E3 Ubiquitin Ligases in Glycogen Solubility Control
One of our lab’s primary projects, recently funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke R01 mechanism, is to identify the role of linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex (LUBAC) in brain-glycogen solubility control. LUBAC is a multi-protein complex composed of two E3 ubiquitin ligases – RBCK1, HOIP – and an adaptor protein, SHARPIN. LUBAC-deficient patients accumulate insoluble glycogen in different organs, especially brain, skeletal, and cardiac muscle, resulting in neurological symptoms, myopathy, and cardiomyopathy with heart failure. This emphasizes LUBAC’s important role in glycogen metabolism. To date, glycogen metabolism-related LUBAC substrate(s) and associated molecular mechanisms are not known. Utilizing newly created mouse models, cell lines, and novel approaches, our current work is testing a central hypothesis that LUBAC keeps the cellular glycogen soluble. Deeper understandings of this LUBAC-mediated control of glycogen metabolism are not only providing new insights towards developing a treatment for a fatal rare condition, but also have implications in other common disease research, such as cancers and Alzheimer’s disease, where both glycogen metabolism and LUBAC are often dysregulated.
Therapeutic Interventions for Glycogen-Metabolism-Related Diseases
At the Mitra lab, we also believe that healing is as equally important as identifying the root cause of any disease. Therefore, we are also interested in developing ideal therapy for neurological conditions using cutting-edge therapeutic interventions such as adeno associated virus-mediated gene replacement therapy or CRISPR-Cas9-mediated gene knockdown therapy. We are also actively collaborating with scientists within and outside of UT Southwestern to identify the best delivery options for these therapeutics to ‘difficult to reach’ organs, such as the brain.