Chromatin regulation in neural development, autistic disorders, and cancer.
Epigenetic regulation plays important roles in stem cell differentiation, tissue development and tumorigenesis. We are interested in the function of chromatin regulation of signaling pathways important for neural development, brain tumor growth and autism pathogenesis. In addition to the traditional genetic, molecular and biochemical methods, we are employing advanced proteomic and genomic approaches to improve our understanding of the transcriptional regulation of these developmental important and cancer-related signaling pathways at the chromatin level. Our studies are mainly focused on two areas.
Project I. Chromatin remodeling of neuronal activity-induced genes and its function in autistic brain disorders.
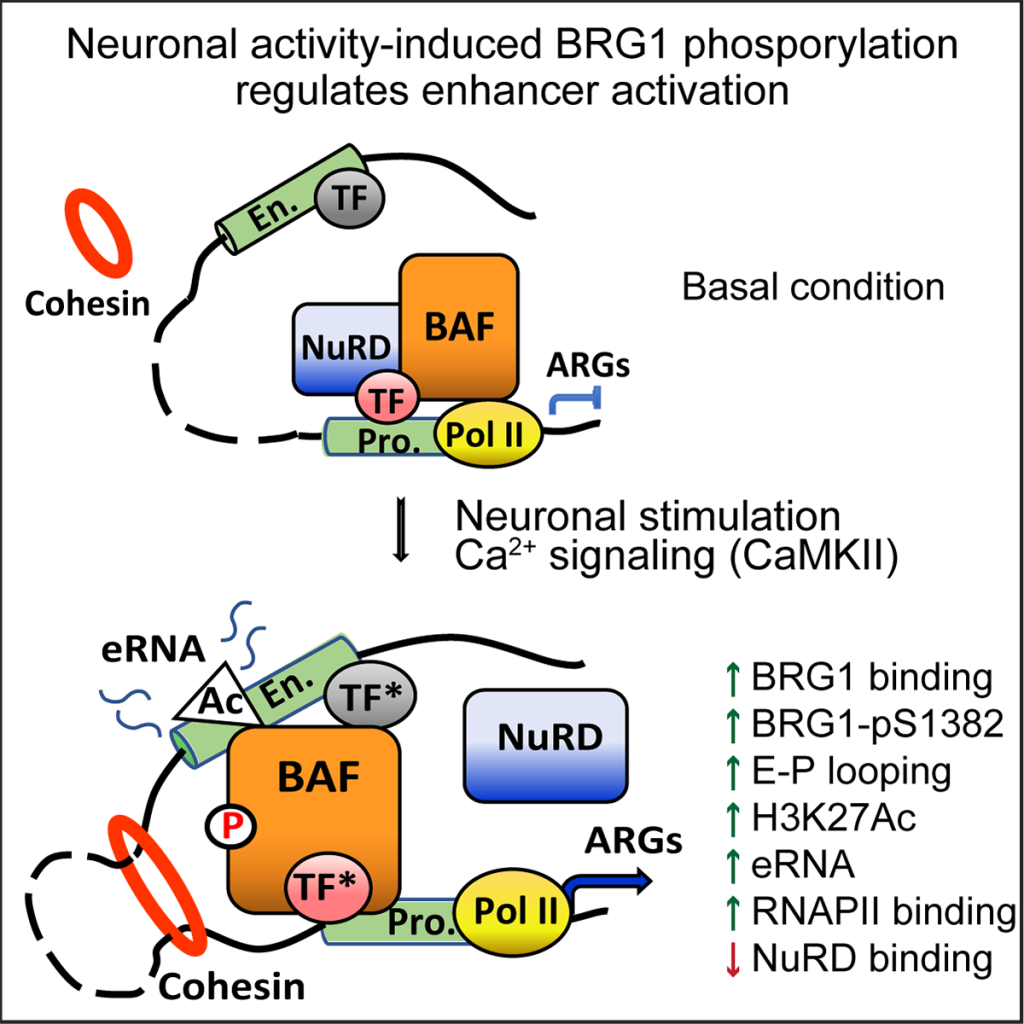
The SWI/SNF-like chromatin remodeling BAF complexes, which regulate gene expression by modulating chromatin structures, have been linked to autism spectrum disorders. The core subunit BRG1/SMARCA4 was predicted to be a key player in the autism gene network. Previously, we showed that neuronal BAF complex is required for synapse development and activity-induced gene expression and neuronal plasticity. Recently, we identified a novel neuronal activity-induced BRG1 phosphorylation site. We showed that BRG1 phosphorylation is required for the activation of neuronal enhancers, expression of key activity-induced genes, and normal mouse stress responses. Currently, using a combination of genetic, genomic, proteomic, and molecular approaches, we are studying (1) how BRG1 and its phosphorylation regulate neuronal enhancer architecture and activities, and (2) how altered BRG1 phosphorylation affects neural development, neuronal functions and animal behaviors.
Kim B, Luo Y, Zhan X, Zhang Z, Shi X, Yi J, Xuan Z, Wu J (2021) Neuronal Activity-Induced BRG1 Phosphorylation Regulates Enhancer Activation. Cell reports, 36(2):109357. PMID: 34260936.
Zhang Z, Cao M, Chang CW, Wang C, Shi X, Zhan X, Birnbaum SG, Bezprozvanny I, Huber K, Wu JI (2015) Autism-associated Chromatin Regulator Brg1/SmarcA4 is Required for Synapse Development and MEF2-mediated Synapse Remodeling. MCB, PMID:26459759.
Wu, J. I., Lessard, J., Olave, I. A., Qiu, Z. Ghosh, A., Graef, I. A., and Crabtree, G. R. (2007). Regulation of dendritic development by neuron-specific chromatin remodeling complexes. Neuron 56, 94-108. PMID:17920018
Project II. Epigenetic regulation of SHH signaling, cerebellar development and medulloblastoma.
Sonic Hedgehog (SHH) signaling is required for the proliferation of cerebellar granule neuron precursor (CGNP) cells. Abnormally activated SHH signaling causes CGNP over-proliferation and medulloblastoma. In the last decade, we identified a dynamic epigenetic network including chromatin remodeling factors and histone modification enzymes that play essential role in regulating SHH signaling transcription outcomes. Using mouse models of SHH-type medulloblastoma and conditional deletions of key epigenetic regulators, we uncovered diverse SHH-dependent and SHH-independent epigenetic mechanisms underlying cerebellar development and SHH medulloblastoma growth. Recently, we reported a novel oncogenic function of epigenetic heterogeneity in medulloblastoma development. These findings may guide us to develop novel treatment strategies for medulloblastoma patients. Our current study on epigenetic regulation of medulloblastoma is supported by a new CPRIT grant.
Yi J, Kim B, Shi X, Zhan X, Lu QR, Xuan Z, Wu J (2022) PRC2 heterogeneity drives tumor growth in medulloblastoma. Cancer Research. PMID: 3573192
Yi J, Xuan Z, Wu J (2020) Histone Demethylase UTX/KDM6A Enhances Tumor Immune Cell Recruitment, Promotes Differentiation and Suppresses Medulloblastoma. Cancer Letters. 2020 PMID: 33253789
Shi X, Wang Q, Gu J, Xuan Z, and Wu JI (2016) SMARCA4/Brg1 Coordinates Genetic and Epigenetic Networks Underlying SHH-type Medulloblastoma Development. Oncogene, doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.108. PMID:27065321
Shi X, Zhang Z, Zhan X, Cao M, Satoh T, Akira S, Shpargel K, Magnuson T, Li Q, Wang R, Wang C, Ge K, Wu JI (2014) An epigenetic switch induced by Sonic hedgehog signaling regulates gene activation during development and medulloblastoma growth. Nat Commun. 5: 5425. PMID:25370275

