Unlocking the Role of LncRNAs in Regulating Organelle Metabolic Function, Inter-Organelle, and Cell-Cell Communication in the Intestinal Tract
Research Area 1
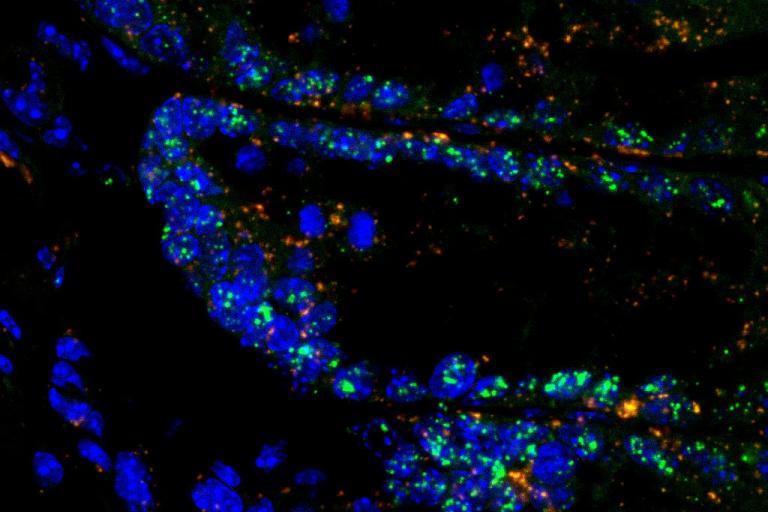
While lncRNAs have been associated with various biological processes, only a handful of lncRNAs have been demonstrated to localize to organelles and regulate their function. How lncRNAs translocate inside organelles, how they modulate immunometabolism, and how they affect the outcome of inflammatory diseases are areas of focus in our lab.
Our lab focuses on answering the following questions:
- Identify the Regulatory Mechanisms Controlling the Expression of lncRNAs in the Colon and Their Trafficking to the Mitochondria
- Uncovering the Enigmatic lncRNAs Shaping the Landscape of Ulcerative Colitis through the Regulation of Innate Immunity
- Identify novel organelle-residing lncRNAs and characterize their impact on cellular and organismal metabolism.
Microbiota-Mediated Post-Translational Regulation of Innate Immune Proteins: Its Influence on Tissue Homeostasis and Disease
Research Area 2
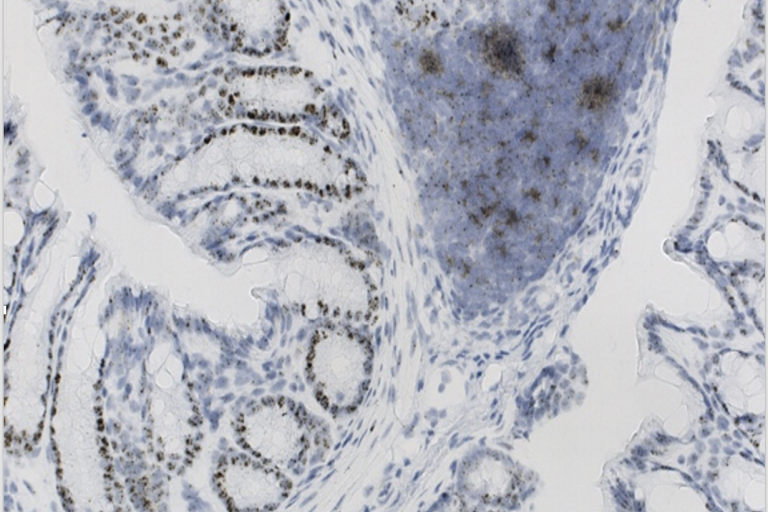
Our lab is dedicated to exploring the captivating world of host-microbiota interactions, with a primary focus on how microbiota regulate immune proteins through post-translational modifications. These intricate mechanisms dictate the activation or silencing of immune proteins, profoundly influencing tissue homeostasis and disease outcomes.
We are interested in how microbiota-driven post-translational modifications shape responses to infections and contribute to cancer development.
We are focusing on addressing the following questions:
- How do gut microbiota regulate post-translational modifications of innate immune proteins, and what are the implications for colon homeostasis and disease?
- How do gut microbiota influence protein stability and function in other organelles, such as the lung and brain, and how does this impact tissue function?
- How does the tumor microbiota influence post-translational modifications of tumor-associated macrophages, and how does it affect the onset and progression of cancer?