Tissue-Mimicking Phantom for Liver Fat Quantification
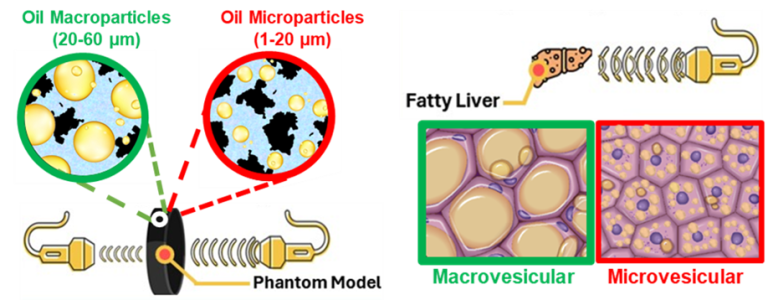
We have developed an innovative methodology for creating ultrasound phantoms that replicate the fat vesicle size characteristic of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD). Our approach utilizes agar-based phantoms embedding stable peanut oil droplets as analogs for lipid vacuoles, effectively simulating fat accumulation in steatotic hepatocytes. These phantoms offer significant potential for validating quantitative imaging methods, particularly ultrasound-based diagnostic tools. Ultimately, our goal is to improve screening, diagnosis, patient management, and treatment response for individuals with metabolic syndrome and MASLD.
Selected Publications
Lipid Microparticle-Based Phantoms Modeling Hepatic Steatosis for the Validation of Quantitative Imaging Techniques, Small Methods, 2025. https://doi.org/10.1002/smtd.202500043
We have developed an innovative methodology for creating ultrasound phantoms that replicate the fat vesicle size characteristic of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD).