A unique feature of ALF and ALI is that there are a variety of causes, all of which share similar clinical features (coagulopathy, encephalopathy, susceptibility to infection, and bleeding) regardless of cause.
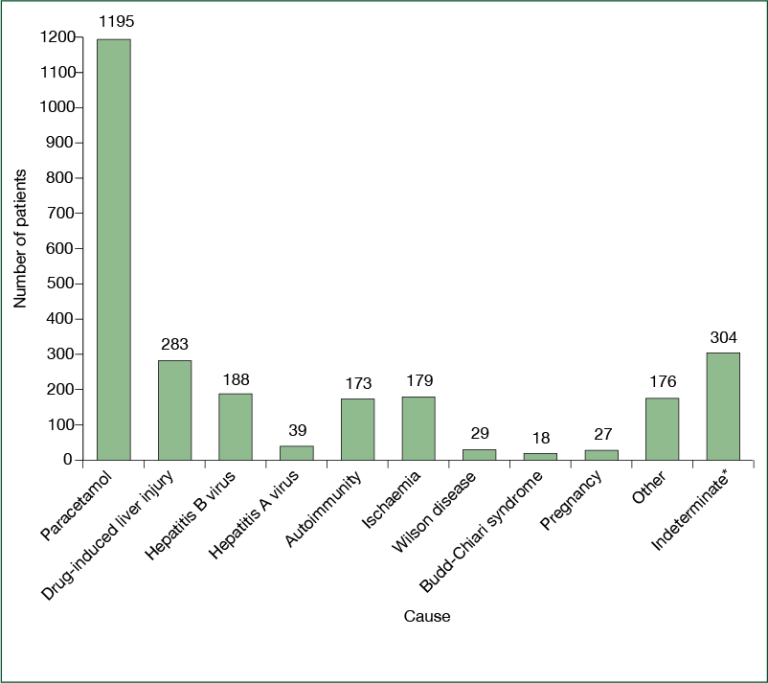
The most common cause (etiology) of ALF in North America is acetaminophen liver toxicity, in most instances the result of overdosing at a single time point (suicide attempt) or over time when seeking pain relief (unintentional overdose). Acetaminophen a very common pain reliever found in innumerable over-the-counter medications (Tylenol®, Nyquil®, TylenolPM®) and prescription opioid combination medications (Vicodin®, Percocet®).
Since APAP is a dose-related toxin, most severe liver injuries are the result of dosing above the recommended package labeling. However, there may be some instances where acetaminophen taken within the package instructions can cause severe acute liver injury and even fatalities. Other causes of ALF include toxicity secondary to prescription drugs, herbal and dietary supplements, and hepatitis A and B. In a small percentage of cases (less than 10%) the cause cannot be delineated (indeterminate).
The most common cause (etiology) of ALF in North America is acetaminophen liver toxicity, in most instances the result of overdosing at a single time point (suicide attempt) or over time when seeking pain relief (unintentional overdose). Acetaminophen a very common pain reliever found in innumerable over-the-counter medications (Tylenol®, Nyquil®, TylenolPM®) and prescription opioid combination medications (Vicodin®, Percocet®).
Since APAP is a dose-related toxin, most severe liver injuries are the result of dosing above the recommended package labeling. However, there may be some instances where acetaminophen taken within the package instructions can cause severe acute liver injury and even fatalities. Other causes of ALF include toxicity secondary to prescription drugs, herbal and dietary supplements, and hepatitis A and B. In a small percentage of cases (less than 10%) the cause cannot be delineated (indeterminate).
Each year, ALF affects approximately 2,000 people in the U.S., while ALI affects 2,000 to 4,000 individuals. Among ALF patients:
- 29% die,
- 22% undergo liver transplantation,
- 51% survive and typically recover fully.