February 2024
Jui-Yu joins the Liou lab
Jui-Yu is joining the Liou lab as an visiting student from National Taiwan University. Welcome Jui-Yu!
June 2023
Wei-Ting joins the Liou lab
Wei-Ting is joining the Liou lab as a research associate. Welcome Wei-Ting!
April 2021
Carlo has a new position
Congratulations of Carlo's new position in NIH as a health scientist. Best wishes for your new job!
April 2021
Carlo received his Ph.D.
Congratulations to Carlo for obtaining his Ph.D. in Cell and Molecular Biology.
August 2020
Chi-Lun has a new position
Congratulations of Chi-Lun's new position in the Department of Cell and Molecular Biology at St. Jude Children's Research Hospital! Best wishes for your new job!
July 2020
Hannes joins the Liou lab
Hannes is joining the Liou lab as a graduate student in the Cell and Molecular Biology Program. Welcome Hannes!
July 2020
Carlo is a trainee of cancer biology T32
Congratulations to Carlo for being selected as a trainee on the NCI Cancer Biology T32 grant.
February 2020
Yu-Ju has a new position
Congratulations of Yu-Ju's new position at Pfizer! Best wishes for your new job!
May 2019
Carlo receives a poster award
Congratulations to Carlo for receiving the 2nd place award of poster competition at the Physiology Departmental Retreat!
November 2018
GFP-MAPPER is available at Addgene
Liou Lab has deposited GFP-MAPPER to Addgene for easy access to all researchers.
July 2018
Ting-Sung receives his Ph.D.
Congratulations to Ting-Sung for obtaining his Ph.D. in Molecular Biophysics. Good luck in the Tagliabracci lab!
May 2018
Yu-Ju gives a talk at the Physiology Departmental Retreat
Congratulations to Yu-Ju for being selected to give a talk at the Physiology Departmental Retreat!
May 2018
Ting-Sung and Wan-Ru receive a poster award
Congratulations to Ting-Sung and Wan-Ru for receiving a poster award at the Physiology Departmental Retreat!
March 2018
Chi-Lun’s paper is published in Journal of Cell Biology
EB1 binding restricts STIM1 translocation to ER–PM junctions and regulates store-operated Ca2+ entry. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Ca2+ sensor STIM1 forms oligomers and translocates to ER–plasma membrane (PM) junctions to activate store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE) after ER Ca2+ depletion. STIM1 also interacts with EB1 and dynamically tracks microtubule (MT) plus ends. Nevertheless, the role of STIM1–EB1 interaction in regulating SOCE remains unresolved. Using live-cell imaging combined with a synthetic construct approach, we found that EB1 binding constitutes a trapping mechanism restricting STIM1 targeting to ER–PM junctions. We further showed that STIM1 oligomers retain EB1 binding ability in ER Ca2+-depleted cells. By trapping STIM1 molecules at dynamic contacts between the ER and MT plus ends, EB1 binding delayed STIM1 translocation to ER–PM junctions during ER Ca2+ depletion and prevented excess SOCE and ER Ca2+ overload. Our study suggests that STIM1–EB1 interaction shapes the kinetics and amplitude of local SOCE in cellular regions with growing MTs and contributes to spatiotemporal regulation of Ca2+ signaling crucial for cellular functions and homeostasis.
March 2018
Jen is promoted to Associated Professor with Tenure
December 2017
Ting-Sung gives a talk at the ASCB meeting
Congratulations to Ting-Sung for being selected to give a talk on “Spatial organization of ER-PM junctions revealed by super- and high-resolution imaging”, in the Minisymposium entitled “Organelle Morphogenesis, Targeting, and Distribution” under the topic Organelles and Membrane Dynamics, at the 2017 American Society for Cell Biology (ASCB) Annual meeting in Philadelphia, PA!
November 2017
Ting-Sung receives the GSO Travel Award
Congratulations to Ting-Sung for receiving the UT Southwestern Graduate Student Organization (GSO) Travel Award. He will use the fund to travel to the ASCB meeting in Philadelphia in December!
November 2017
Yu-Ju gives a talk at the Cell and Molecular Biology Retreat
Congratulations to Yu-Ju for being selected to give a talk at the annual retreat of the Cell and Molecular Biology Graduate Program of UT Southwestern!
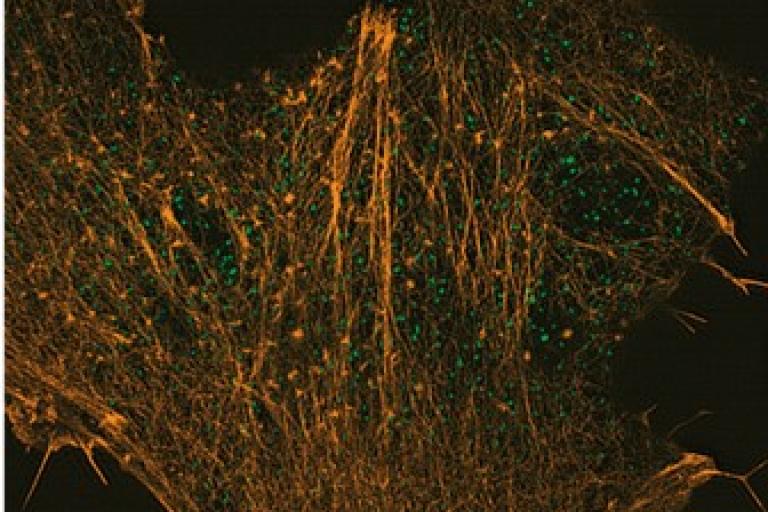
September 2017
Ting-Sung’s paper is published in the Special Issue on Quantitative Cell Biology of Molecular Biology of the Cell
Cortical actin contributes to spatial organization of ER–PM junctions. Endoplasmic reticulum–plasma membrane (ER–PM) junctions mediate crucial activities ranging from Ca2+ signaling to lipid metabolism. Spatial organization of ER–PM junctions may modulate the extent and location of these cellular activities. However, the morphology and distribution of ER–PM junctions are not well characterized. Using photoactivated localization microscopy (PALM), we reveal that the contact area of single ER–PM junctions is mainly oblong with the dimensions of ∼120 nm × ∼80 nm in HeLa cells. Using total internal reflection fluorescence (TIRF) microscopy and structure illumination microscopy (SIM), we show that cortical actin contributes to spatial distribution and stability of ER–PM junctions. Further functional assays suggest that intact F-actin architecture is required for phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate homeostasis mediated by Nir2 at ER–PM junctions. Together, our study provides quantitative information on spatial organization of ER–PM junctions that is in part regulated by F-actin. We envision that functions of ER–PM junctions can be differentially regulated through dynamic actin remodeling during cellular processes.
August 2017
Carlo is elected as the GSO President
Congratulations to Carlo for being elected as the President of the Graduate Student Organization (GSO) at UT Southwestern!
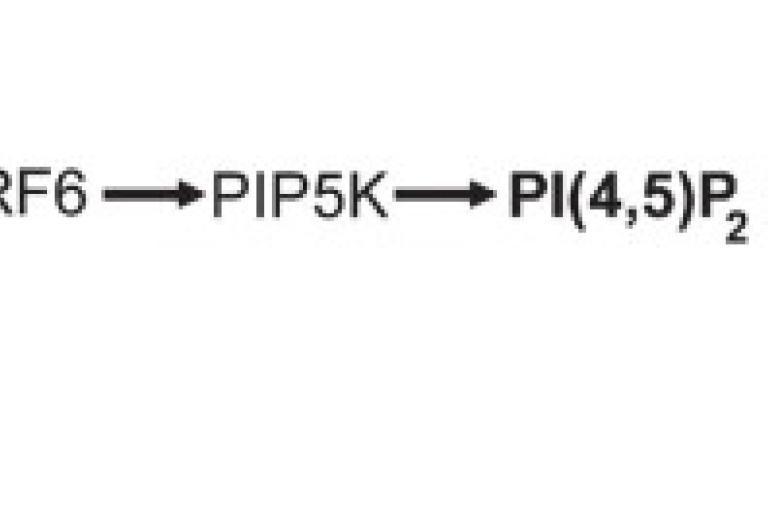
June 2017
Yu-Ju’s paper is published in Journal of Cell Biology
RASSF4 controls SOCE and ER–PM junctions through regulation of PI(4,5)P2. RAS association domain family 4 (RASSF4) is involved in tumorigenesis and regulation of the Hippo pathway. In this study, we identify new functional roles of RASSF4. First, we discovered that RASSF4 regulates store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE), a fundamental Ca2+ signaling mechanism, by affecting the translocation of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Ca2+ sensor stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1) to ER–plasma membrane (PM) junctions. It was further revealed that RASSF4 regulates the formation of ER–PM junctions and the ER–PM tethering function of extended synaptotagmins E-Syt2 and E-Syt3. Moreover, steady-state PM phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PI[4,5]P2) levels, important for localization of STIM1 and E-Syts at ER–PM junctions, were reduced in RASSF4-knockdown cells. Furthermore, we demonstrated that RASSF4 interacts with and regulates the activity of adenosine diphosphate ribosylation factor 6 (ARF6), a small G protein and upstream regulator of type I phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinases (PIP5Ks) and PM PI(4,5)P2 levels. Overall, our study suggests that RASSF4 controls SOCE and ER–PM junctions through ARF6-dependent regulation of PM PI(4,5)P2 levels, pivotal for a variety of physiological processes.
December 2016
Yu-Ju gives a talk at the ASCB meeting
Congratulations to Yu-Ju for being selected to give a talk on “RASSF4 regulates PIP2 and formation of ER-PM junctions”, in the Minisymposium entitled “Organelle Contact Sites and Biogenesis” under the topic Organelles and Spatial Organization of the Cell, at the 2016 American Society for Cell Biology (ASCB) Annual meeting in San Francisco, CA!
September 2016
Yu-Ju receives the ASCB Postdoctoral Research Travel Award
Congratulations to Yu-Ju for being selected as a recipient of the ASCB Postdoctoral Research Travel Award! She is going to the ASCB meeting in San Francisco to present her work in December!
July 2016
Carlo receives the Great Lakes National Scholarship
Congratulations to Carlo for receiving the Great Lakes National Scholarship for graduate students pursuing STEM-related degrees!
June 2016
Wan-Ru joins the Liou lab
Wan-Ru Lee is joining the Liou lab as a research scientist and lab manager. Welcome Wan-Ru!
February 2016
Chi-Lun has a new position
Chi-Lun is joining the Lippincott-Schwartz Lab at the HHMI Janelia Research Campus as a Postdoctoral Associate. Good luck in your new lab!
January 2016
Carlo joins the Liou lab
Carlo is joining the Liou lab as a graduate student in the Cell and Molecular Biology Program. Welcome Carlo!
June 2015
Jen receives an NIH RO1 Award
Jen is awarded a five-year NIH RO1 Grant on her application entitled “Functions and Regulation of Endoplasmic Reticulum-Plasma Membrane Junctions”.
April 2015
Jen receives a Welch Foundation Award
Jen is awarded a three-year Welch Foundation Grant on her application entitled “Novel Imaging Probes for Investigating ER Membrane Contact Sites”.
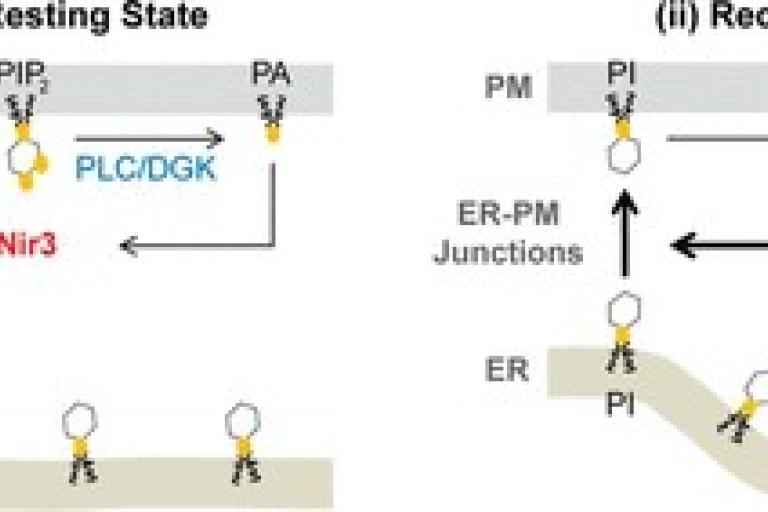
April 2015
Chi-Lun’s paper is published in Journal of Biological Chemistry.
PIP2 Homeostasis Regulated by Nir2 and Nir3 Proteins at ER–PM junctions. Phosphatidylinositol (PI) 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) at the plasma membrane (PM) constitutively controls many cellular functions, and its hydrolysis via receptor stimulation governs cell signaling. The PI transfer protein Nir2 is essential for replenishing PM PIP2 following receptor-induced hydrolysis, but key mechanistic aspects of this process remain elusive. Here, we demonstrate that PI at the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is required for the rapid replenishment of PM PIP2 mediated by Nir2. Nir2 detects PIP2 hydrolysis and translocates to ER-PM junctions via binding to phosphatidic acid. With distinct phosphatidic acid binding abilities and PI transfer protein activities, Nir2 and its homolog Nir3 differentially regulate PIP2 homeostasis in cells during intense receptor stimulation and in the resting state, respectively. Our study reveals that Nir2 and Nir3 work in tandem to achieve different levels of feedback based on the consumption of PM PIP2 and function at ER-PM junctions to mediate nonvesicular lipid transport between the ER and the PM.
December 2014
Chi-Lun gives a talk at the ASCB meeting
Congratulations to Chi-Lun for being selected to give a talk on “Differential regulation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate homeostasis by Nir2 and Nir3 at ER-Plasma membrane junctions”, in the Minisymposium entitled “Small GTPases and Lipids in Membrane Dynamics” under the topic Membrane Traffic: Dynamics and Regulation at the 2014 American Society for Cell Biology (ASCB) Annual meeting in Philadelphia, PA!
May 2014
Chi-Lun receives his Ph.D.
Congratulations to Chi-Lun for obtaining his Ph.D. in Integrative Biology (Mechanisms of Disease Track)!
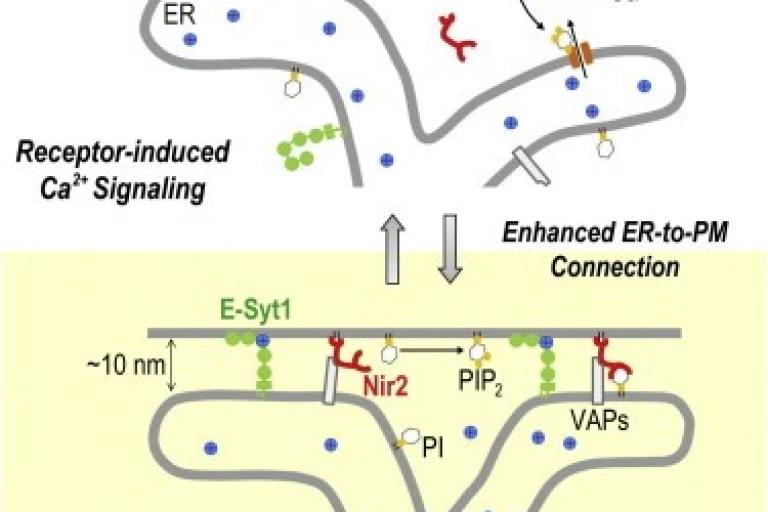
November 2013
Chi-Lun’s paper is published in Cell Reports
Feedback Regulation of Receptor-Induced Ca2+ Signaling Mediated by E-Syt1 and Nir2 at ER-PM Junctions. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-plasma membrane (PM) junctions are highly conserved subcellular structures. Despite their importance in Ca2+ signaling and lipid trafficking, the molecular mechanisms underlying the regulation and functions of ER-PM junctions remain unclear. By developing a genetically encoded marker that selectively monitors ER-PM junctions, we found that the connection between ER and PM was dynamically regulated by Ca2+ signaling. Elevation of cytosolic Ca2+ triggered translocation of E-Syt1 to ER-PM junctions to enhance ER-to-PM connection. This subsequently facilitated the recruitment of Nir2, a phosphatidylinositol transfer protein (PITP), to ER-PM junctions following receptor stimulation. Nir2 promoted the replenishment of PM phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) after receptor-induced hydrolysis via its PITP activity. Disruption of the enhanced ER-to-PM connection resulted in reduced PM PIP2 replenishment and defective Ca2+ signaling. Altogether, our results suggest a feedback mechanism that replenishes PM PIP2 during receptor-induced Ca2+ signaling via the Ca2+ effector E-Syt1 and the PITP Nir2 at ER-PM junctions.
March 2013
Ting-Sung joins the Liou lab
Ting-Sung is joining the Liou lab as a graduate student in the Molecular Biophysics Program. Welcome Ting-Sung!
February 2013
Yu-Ju joins the Liou lab
Yu-Ju is joining the Liou lab as a postdoctoral fellow supported by a two-year Postdoctoral Fellowship from Taiwan National Science Council. Welcome Yu-Ju!