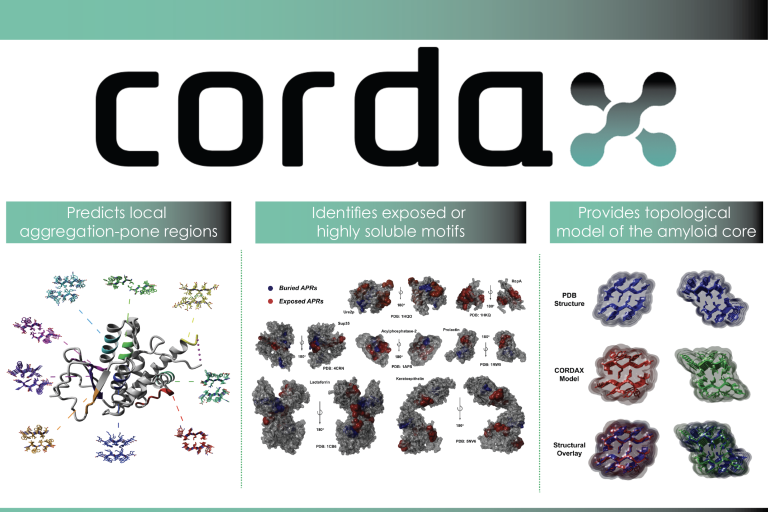

Cordax
Cordax is a structure-based machine learning approach that explores sequence determinants of amyloid propensity beyond their traditional limits.
To achieve this, Cordax translates structural compatibility and interaction energies into sequence aggregation propensity.
When used, please cite:
1. Louros N, Orlando G, De Vleeschouwer M, Rousseau F, Schymkowitz J (2020) Structure-based machine-guided mapping of amyloid sequence space reveals uncharted sequence clusters with higher solubilities. Nature Communications 11, 3314.
2. Louros N. et al. (2024) CORDAX web server: An online platform for the prediction and 3D visualization of aggregation motifs in protein sequences. Bioinformatics, btae279.
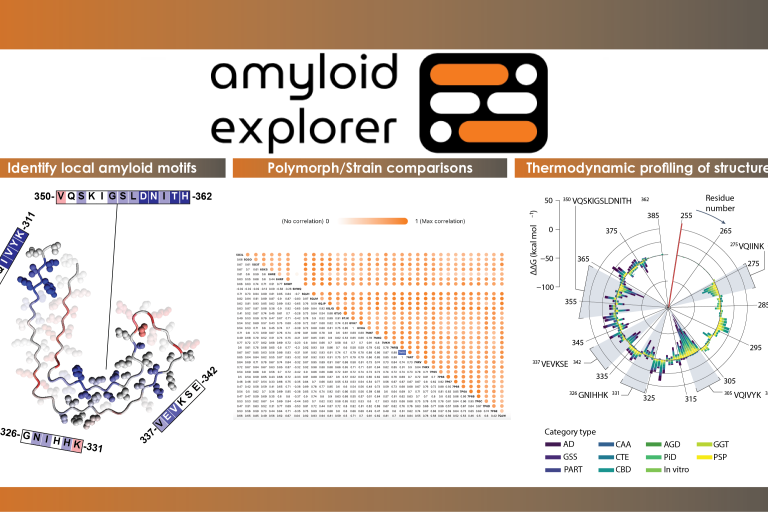
Welcome to Amyloid Explorer!
Amyloid Explorer is a public repository for structural analysis of full-length amyloid fibril core structures. This tool supports the structural analysis of amyloid fibrils based on similarities in disease type, structural layout and thermodynamic profiling.
When used, please cite:
1. Kyriazis V, Gadhe L, Konstantoulea K, Louros N*, Schymkowitz J*, Rousseau F*. (2025) Amyloid Explorer: a global atlas of amyloid fibril structures and thermodynamic principles. bioRxiv, 2025.10.15.682595; doi.org/10.1101/2025.10.15.682595.
2. Louros N, van der Kant R, Rousseau F, Schymkowitz J. (2022) StAmP-DB: A platform for structures of polymorphic amyloid fibril cores. Bioinformatics, 38(9):2636-8.
3. van der Kant R, Louros N, Schymkowitz J, Rousseau F. (2022) Thermodynamic analysis of amyloid fibril structures reveals a common framework for stability in amyloid polymorphs. Structure 30(8): 1178-89.
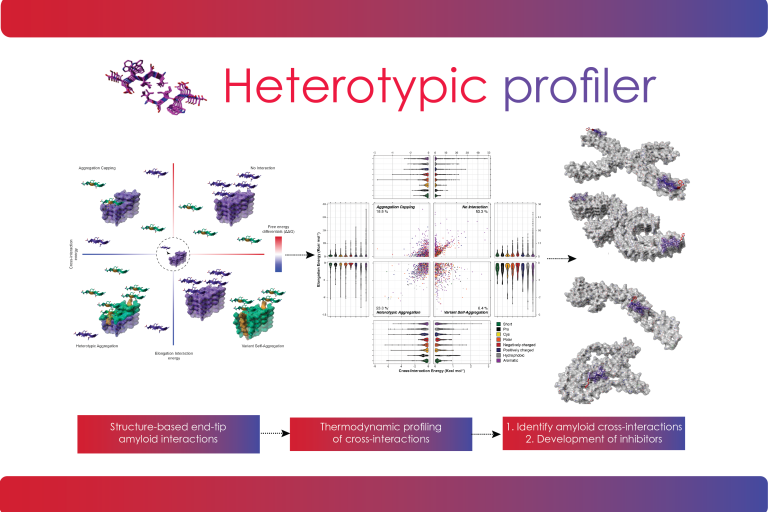
Heterotypic amyloid interactions profiler
This tool uses structure-based thermodynamic calculations to perform a comprehensive exploration of the defining role of sequence promiscuity in amyloid interactions. With this approach, users can estimate the likelihood of cross-aggregation interactions or heterotypic amyloid interactions with other biomolecules. The same approach can be used to tailor the design of inhibitors that aim to block axial amyloid elongation.
When used, please cite:
Louros N, Ramakers M, Michiels E, Konstantoulea K, Morelli C, Garcia T, Moonen N, D’Haeyer S, Goossens V, Thal D, Audenaert D, Rousseau F, Schymkowitz J. (2022) Mapping the sequence specificity of heterotypic amyloid interactions enables the identification of aggregation modifiers. Nature Communications 13, 1351.

Welcome to the WALTZ-DB 2.0!
WALTZ-DB 2.0 is a database for characterizing short peptides for their amyloid fiber-forming capacities. The majority of the data comes from electron microscopy, FTIR and Thioflavin-T experiments done by the Switch lab. Apart from that class of data we also provide the amyloid annotation for several other short peptides found in current scientific research papers. Structural models of the potential amyloid cores are provided for every peptide entry.
We encourage users to help us keep the database up to date by submitting newly identified aggregation-prone peptide sequences using the contact form available online.
When used, please cite:
Louros, N. et al. (2019) WALTZ-DB 2.0: an updated database containing structural information of experimentally determined amyloid-forming peptides. Nucleic Acids Res, 48 (D1), D389–D393. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz758.
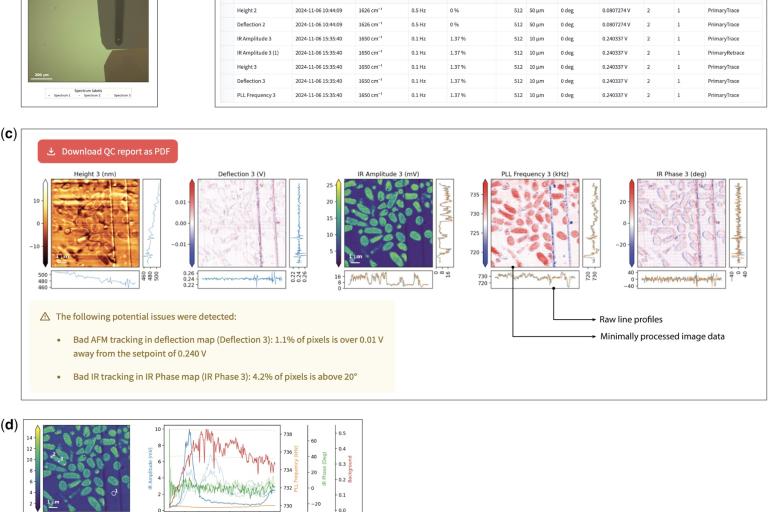
AXZ Viewer
We have developed AXZ Viewer, a web application that allows anyone to open, review, and audit raw AFM-IR data files easily and without deep knowledge of the method. It also exposes all metadata recorded by the microscope at the time of measurement. The web application is based on a Python package that supports custom data analyses within the scientific Python ecosystem. This tool provides an accessible, transparent solution for AFM-IR data review, with the potential to support reproducibility and standardization in AFM-IR research and encourage wider adoption of this innovative spectroscopy method
When used, please cite:
Duverger, W. et al. (2025) AXZ viewer: a web application to visualize unprocessed AFM-IR data. Bioinformatics, 45 (10), btaf513.