Featured Publications
January, 2026
Inhibition of FicD-mediated AMPylation and deAMPylation by Isoprenoid Diphosphates
Aubrie M Blevins, Wei Peng, Lisa N Kinch, Zihan Monshad, Andrea G Paredes, Christina Volz, Jared Rutter, Amanda K Casey, Kevin G Hicks, Kim Orth
Description
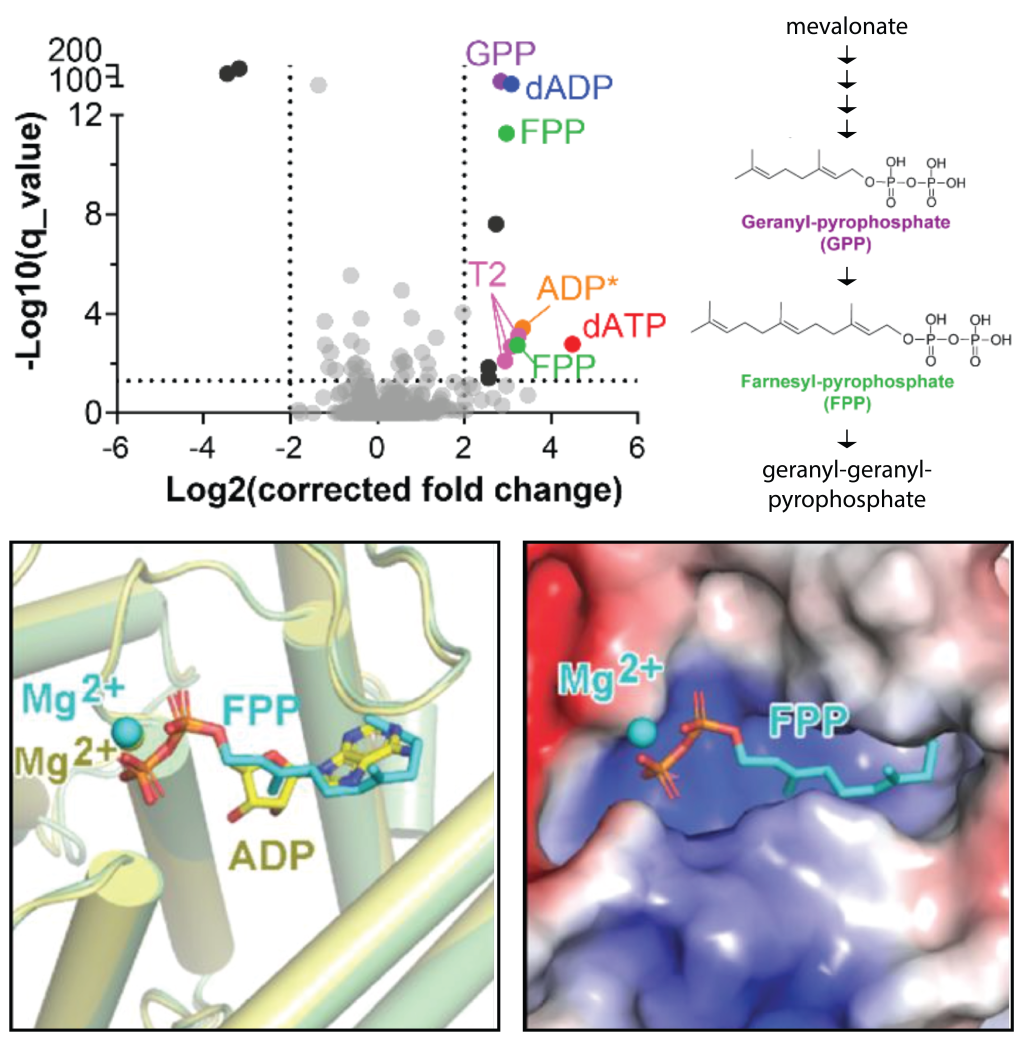
In-vivo regulation of FicD activity remains elusive, and identifying metabolites that alter its activity could prove useful pharmaceutically. We applied an unbiased high-throughput screening platform, known as Mass spectrometry Integrated with equilibrium Dialysis for the discovery of Allostery Systematically (MIDAS), to identify novel small molecule metabolites that might regulate FicD. MIDAS revealed interactions between FicD and two mavelonate pathway intermediates: geranyl-pyrophosphate and farnesyl-pyrophosphate. These metabolites inhibit FicD-mediated AMPylation and deAMPylation, and a crystal structure of FicD bound to farnesyl-pyrophosphate demonstrates a competitive inhibition mechanism. These inhibitors distinguish between FicD variants linked to different human pathologies, providing insight into pharmacological targeting of UPR activity.
August, 2025
A critical role for Vibrio parahaemolyticus LPS to mediate evasion of host immune response during infection
Jananee Jaishankar, Hyojik Yang, Ian P O'Keefe, Brandon M Tenaglia, Lisa N Kinch, Robert K Ernst, Kim Orth
Description
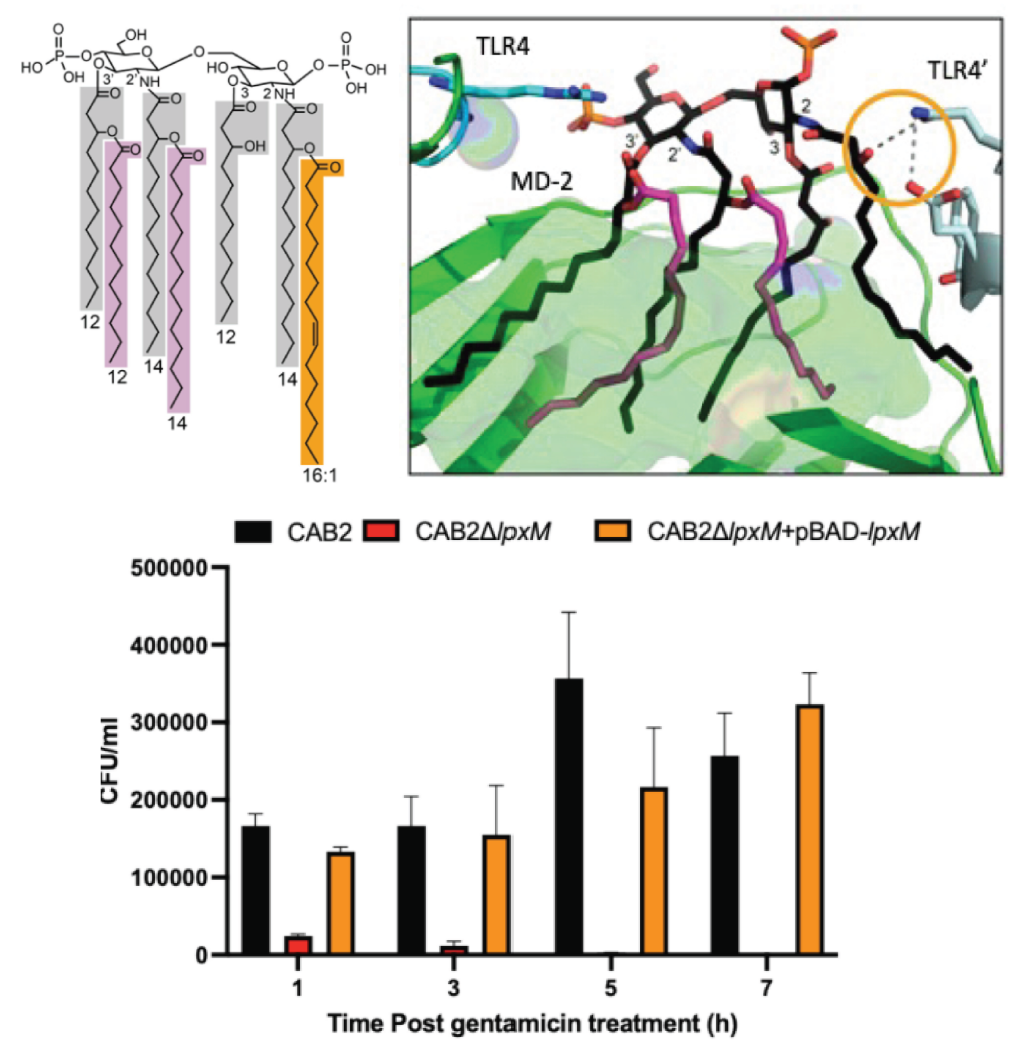
The strategies Vibrio parahaemolyticus (Vpara) employs to circumvent innate immune detection by the host remain poorly understood. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) serves as the major pathogen-associated molecular pattern that triggers host inflammatory responses, and its lipid A structure contributes to the degree of innate immune system activation. We defined this structure in free living Vpara as predominantly hepta-acylated, which elicits a weakened TLR4 immune response as compared to Escherichia coli, allowing V. para entry and replication inside host cells. Deletion of the Vpara lipid A biosynthesis enzyme lpxM alters lipid A secondary acylation, enhancing immune response and impairing replication within epithelial cells. This study provides evidence that the unique Vpara LPS structure plays a crucial role in evading host innate immunity, facilitating the bacterium's intracellular survival.
May, 2025
Pre-clinical model of dysregulated FicD AMPylation causes diabetes by disrupting pancreatic endocrine homeostasis
Amanda K Casey, Nathan M Stewart, Naqi Zaidi, Hillery F Gray, Hazel A Fields, Masahiro Sakurai, Carlos A Pinzon-Arteaga, Bret M Evers, Jun Wu and Kim Orth
Description
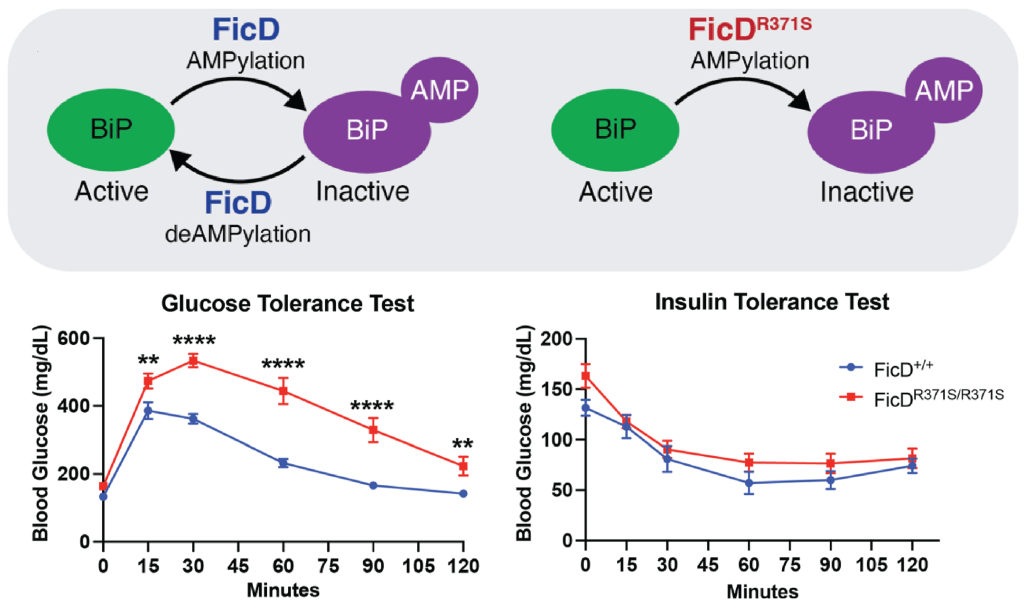
Human hFicD with an R371S mutation disrupts FicD deAMPylation activity resulting in severe neonatal diabetes. We generated the corresponding mutation in mice (mFicDR371S) to create a pre-clinical murine model for neonatal diabetes. The mutant mice displayed elevated BiP AMPylation levels across multiple tissues and signature markers for diabetes including glucose intolerance and reduced serum insulin levels. Adult mFicDR371S mice displayed disturbed pancreatic islet organization that progressed with age. This work provides a preclinical mouse model for the study of UPR associated diabetes and demonstrates the essentiality of FicD for tissue resilience.
January, 2025
Genetic and Microbial Analysis of Invasiveness for Escherichia coli Strains Associated With Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Jungyeon Kim, Jing Zhang, Lisa Kinch, Jinhui Shen, Sydney Field, Shahanshah Khan, Jan-Michael Klapproth, Kevin J Forsberg, Tamia Harris-Tryon, Kim Orth, Qian Cong, Josephine Ni
Description
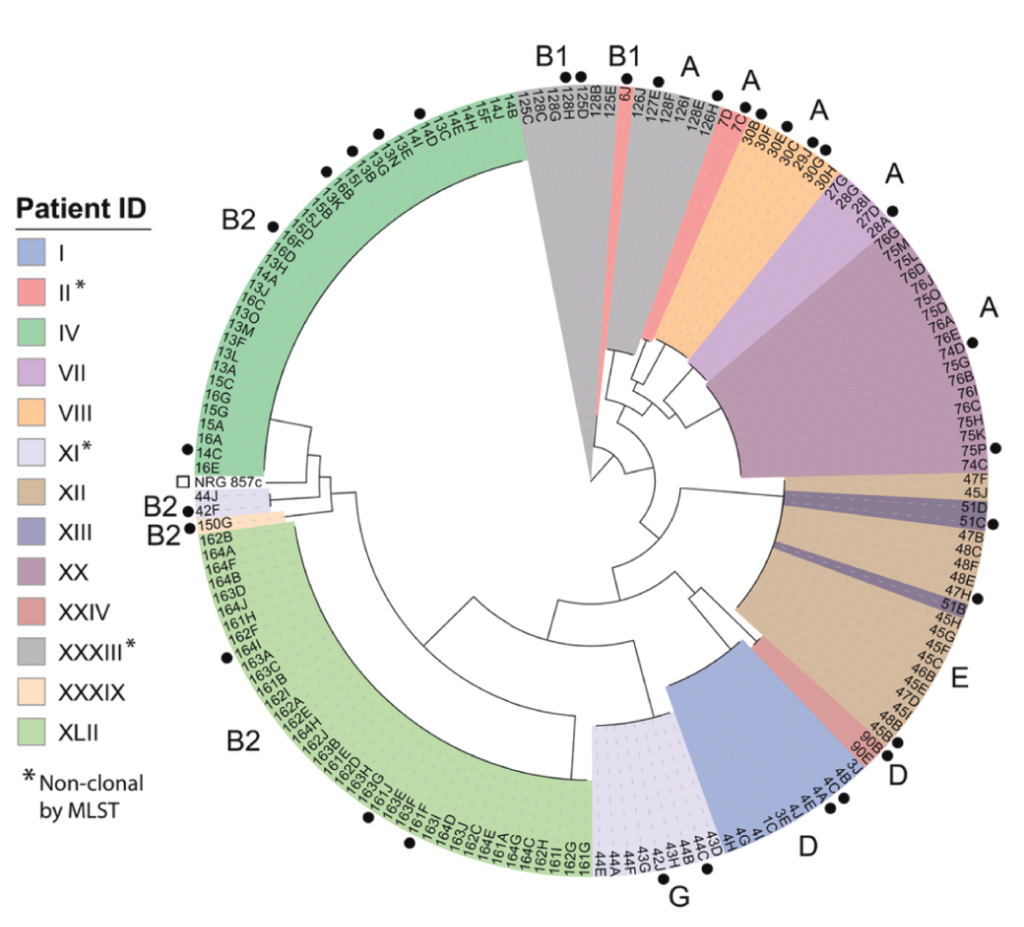
The adherent-invasive Escherichia coli (AIEC) pathotype is thought to contribute to inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) pathogenesis. However, the broad definition of AIEC by phenotype combined with their genetic diversity across patients has complicated the identification of virulence determinates. Thus, we sought to quantify the invasion phenotype of clinical isolates from patients with IBD and identify the genetic basis for their invasion into epithelial cells. Pangenome-wide comparisons of E. coli clinical isolates identified accessory genes that segregate with invasion phenotype. These correlations found the acquisition of antibiotic resistance genes in clinical isolates compromised the traditional gentamicin protection assays used to quantify invasion. A modified invasion assay taking into account resistance identified genes encode an arylsulfatase, a glycoside hydrolase, and genetic islands carrying propanediol utilization and sulfoquinovose metabolism pathways as contributing to invasion.
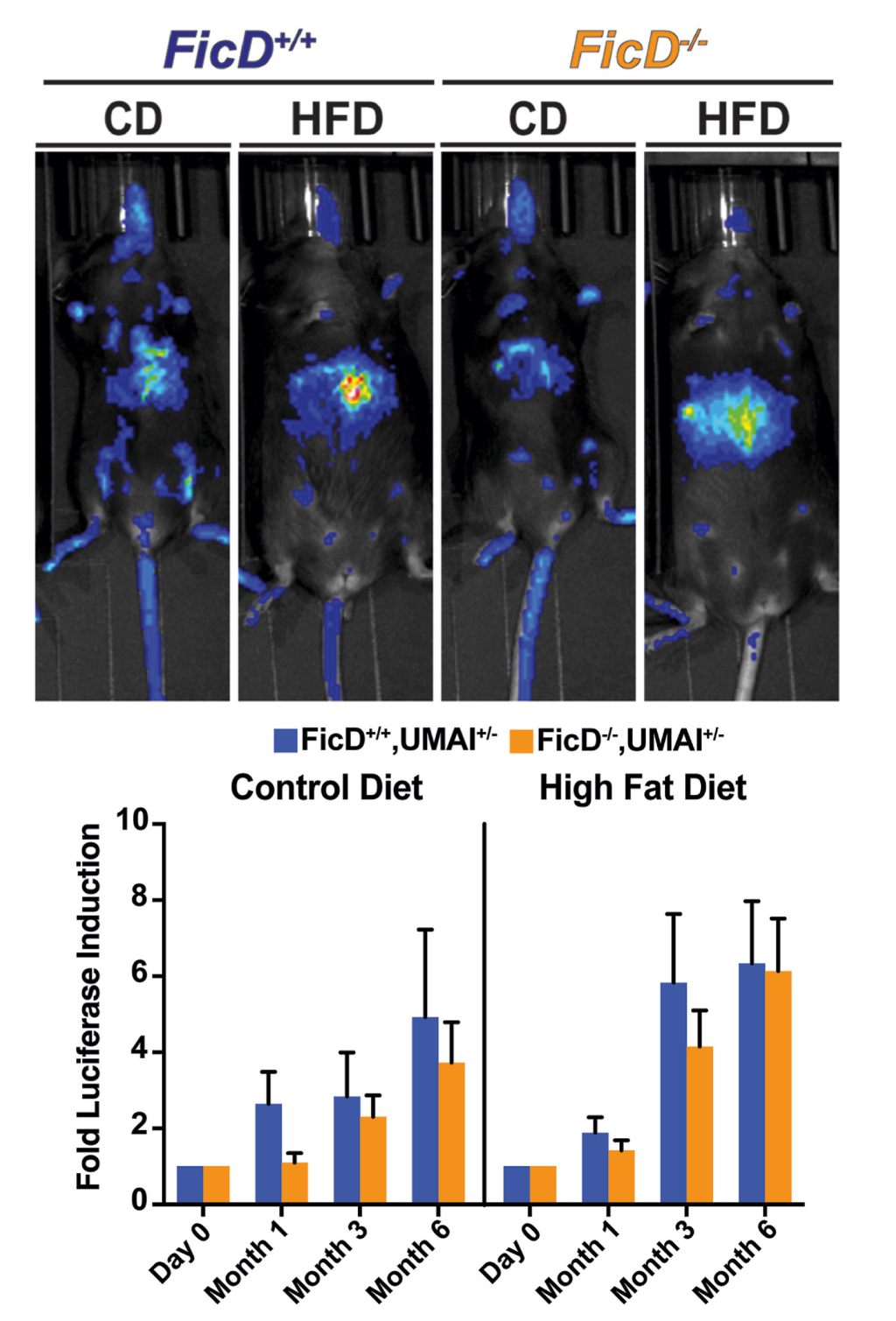
October, 2024
FicD regulates adaptation to the unfolded protein response in the murine liver
Amanda K Casey, Nathan M Stewart, Naqi Zaidi, Hillery F Gray, Amelia Cox, Hazel A Fields, and Kim Orth
Description
The unfolded protein response (UPR) is a cellular stress response that is activated when misfolded proteins accumulate in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). FicD AMPylates BiP during homeostasis and deAMPylates BiP during stress. Here, we find livers lacking FicD exhibit enhanced UPR signaling in response to short term physiologic fasting and feeding stress. The livers of FicD-/- did not show marked changes in UPR signaling or damage after either chronic high fat diet (HFD) feeding or acute pathological UPR induction. Intriguingly, FicD-/- mice showed changes in UPR induction and weight loss patterns following repeated pathological UPR induction. These findings indicate that FicD regulates UPR responses during mild physiological stress and in adaptation to repeated stresses, but there are tissue specific differences in the requirement for FicD regulation.
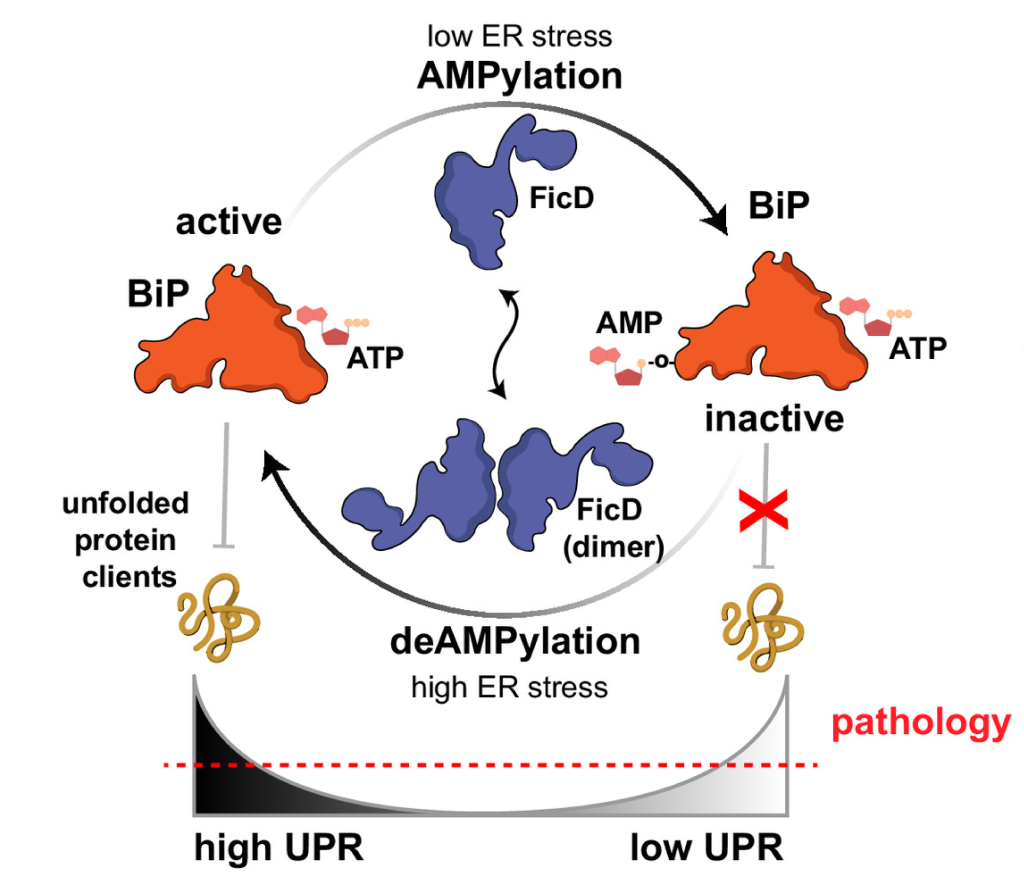
September, 2024
FicD sensitizes cellular response to glucose fluctuations in mouse embryonic fibroblasts.
Burak Gulen, Aubrie Blevins, Lisa Kinch, Kelly A Servage, Nathan M Stewart, Hillery F Gray, Amanda K Casey, and Kim Orth
Description
During homeostasis, the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) maintains productive transmembrane and secretory protein folding that is vital for proper cellular function. The bifunctional enzyme FicD mediates AMPylation and deAMPylation of BiP in response to changes in ER stress. We find differential BiP AMPylation signatures when comparing robust chemical ER stress inducers to physiological glucose starvation stress and recovery in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs). Wildtype MEFs respond to pharmacological ER stress by down-regulating BiP AMPylation, while AMPylation increases upon metabolic stress induced by glucose starvation. Deletion of FicD results in widespread gene expression changes, exhibit dampened UPR signaling, altered cell stress recovery response, and unconstrained protein secretion. Our findings indicate that FicD is important for tampering UPR signaling, stress recovery, and the maintenance of secretory protein homeostasis.
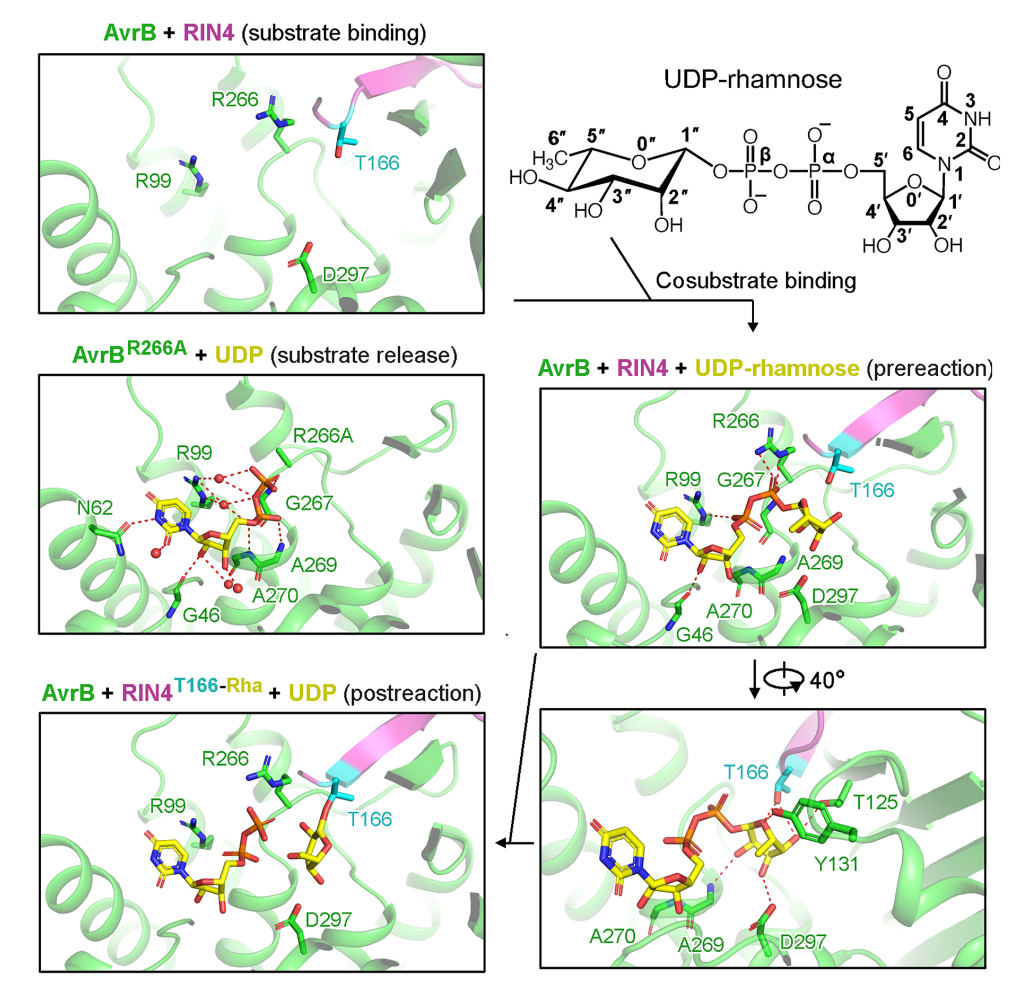
April, 2024
Pseudomonas effector AvrB is a glycosyltransferase that rhamnosylates plant guardee protein RIN4.
Wei Peng, Nalleli Garcia, Kelly A Servage, Jennifer J Kohler, Joseph M Ready, Diana R Tomchick, Jessie Fernandez, and Kim Orth
Description
The plant pathogen Pseudomonas syringae encodes a type III secretion system avirulence effector protein, AvrB, that induces the plant hypersensitive response as a defense mechanism against systemic infection. Despite the well-documented catalytic activities observed in other Fido (Fic, Doc, and AvrB) proteins, the enzymatic activity and target substrates of AvrB have remained elusive. Here, we show that AvrB is a glycosyltransferase that transfers rhamnose from UDP-rhamnose to a threonine residue of the Arabidopsis guardee protein RIN4. We report structures of various enzymatic states of the novel AvrB-catalyzed rhamnosylation reaction of RIN4. Collectively, our results uncover an unexpected reaction performed by a prototypical member of the Fido superfamily while providing important insights into the plant hypersensitive response pathway.
December, 2023
Insights into virulence: structure classification of the Vibrio parahaemolyticus RIMD mobilome.
Lisa Kinch, R. Dustin Schaeffer, Jing Zhang, Qian Cong, Kim Orth, and Nick Grishin
Description
The pandemic Vibrio parahaemolyticus strain RIMD genome encodes pathogenicity islands that contribute to the success of the strain in infection. Based on the EOCD database, we used evolution-based classification of structure models for the RIMD proteome to improve our functional understanding of virulence determinants acquired by the pandemic strain. We further identify and classify previously unknown mobile protein domains as well as fast evolving residue positions in structure models that contribute to virulence and adaptation with respect to a pre-pandemic strain.
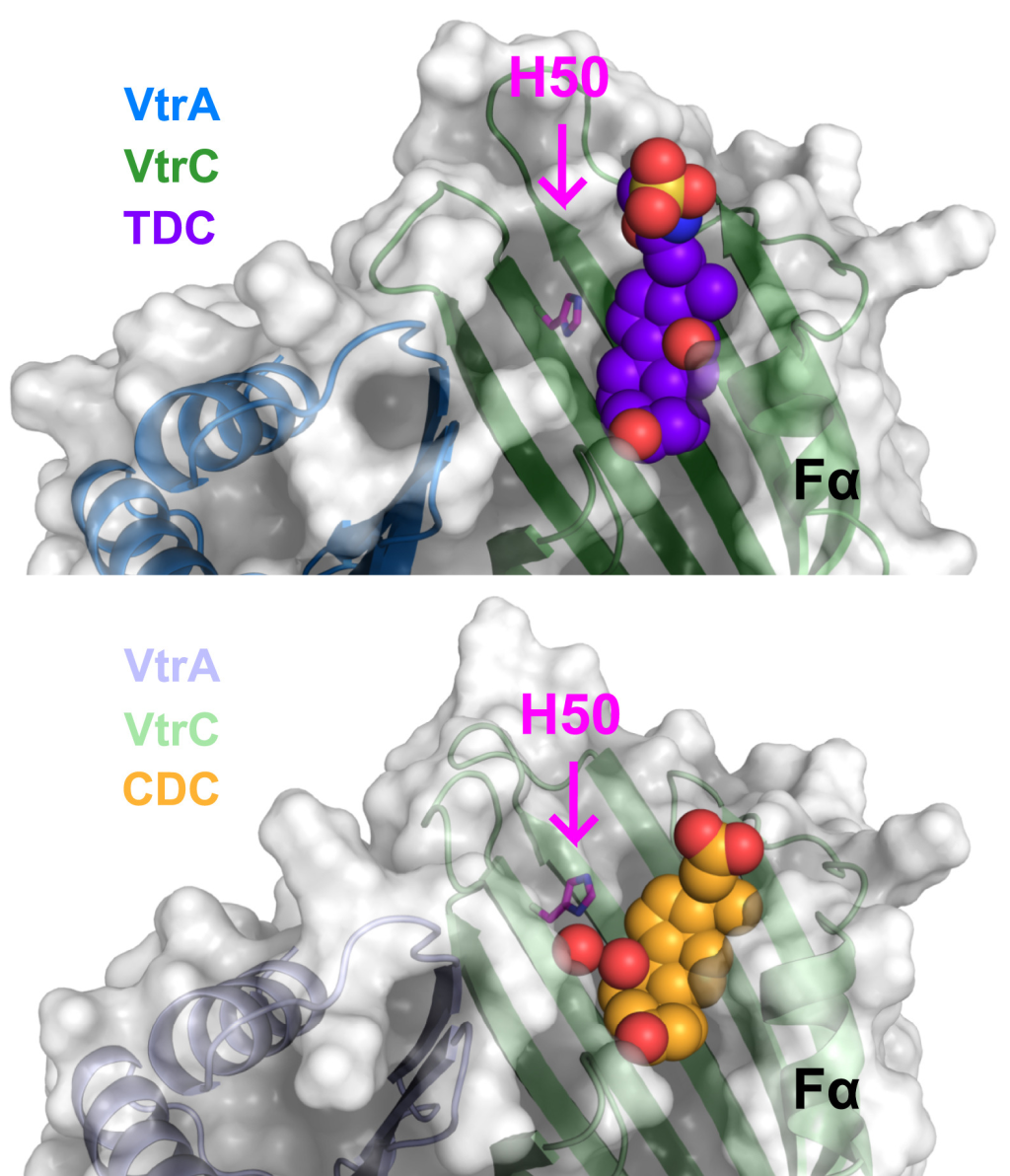
April, 2023
Molecular determinants for differential activation of the bile acid receptor from the pathogen Vibrio parahaemolyticus.
Angela J. Zou, Lisa Kinch, Suneeta Chimalapati, Nalleli Garcia, Diana R. Tomchick, and Kim Orth
Description
Pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus differentially senses bile acids to induce pathogenesis. The bile acid taurodeoxycholate (TDC) activates the VtrB master transcription regulator of the Type III Secretion System (T3SS), whereas other bile acids such as chenodeoxycholate (CDC) do not. We present the crystal structure of the periplasmic VtrA/VtrB receptor bound to CDC, which competes for TDC binding. Using isothermal titration calorimetry, we observed most binding pocket mutants decreased affinity for bile acid. Notably, two mutants bound bile acids with a similar affinity as WT but were attenuated for TDC-induced T3SS activation. Collectively, these studies provide a molecular explanation for the selective pathogenic signaling by V. parahaemolyticus in response to bile acid.
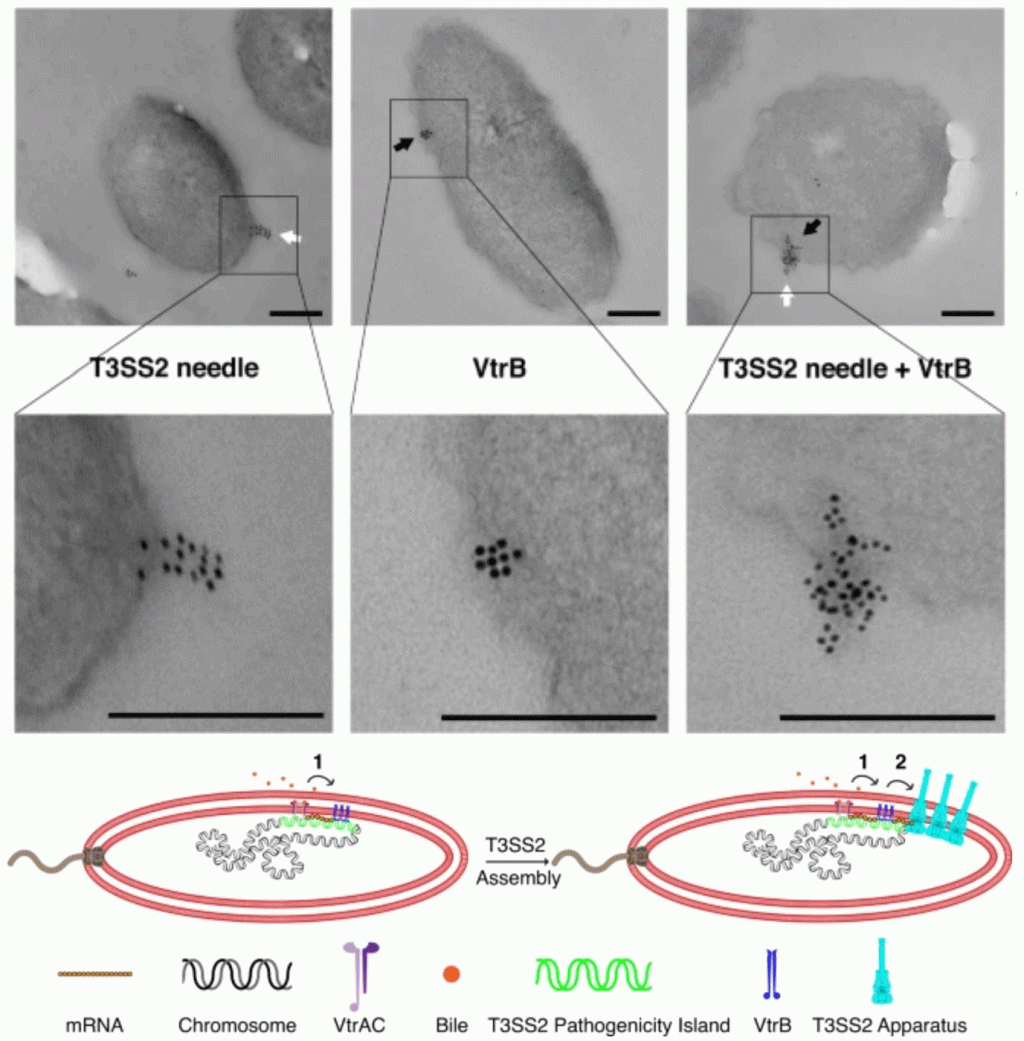
March 2, 2023
Membrane-localized expression, production and assembly of Vibrio parahaemolyticus T3SS2 provides evidence for transertion.
Karan Gautam Kaval, Suneeta Chimalapati, Siegel Sara D., Nalleli Garcia, Jananee Jaishankar, Ankur B. Dalia & Kim Orth
Description
We provide evidence for transertion, the process of coupled transcription, translation and membrane insertion of the Type III Secretion System (T3SS) molecular machine by the bacterial pathogen Vibrio parahaemolyticus. We propose the pathogen accomplishes transertion by a two-step process initiated by the transmembrane co-component signaling system VtrA/VtrC, which turns on expression of a second membrane anchored transcription factor (VtrB) in response to bile acid. VtrB induces the localized expression and membrane assembly of the T3SS2 structural components. Transertion likely allows the efficient assembly of membrane-bound molecular complexes in response to extracellular signals.
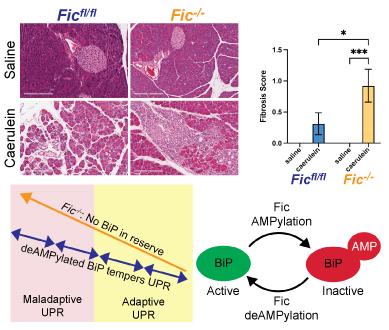
August 1, 2022
Fic-mediated AMPylation tempers the unfolded protein response during physiological stress.
Casey AK, Gray HF, Chimalapati S, Hernandez G, Moehlman AT, Stewart N, Fields HA, Gulen B, Servage KA, Stefanius K, Blevins A, Evers BM, Krämer H, Orth K.
Description
We generated a conditional null allele of the AMPylating enzyme filamentation induced by cyclic-AMP (Fic) in mice and characterized the effect of Fic loss on the exocrine pancreas. We reveal Fic is required in differentiated tissue for the regulation of the unfolded protein response (UPR) during both physiological and pharmacological stresses. We also propose that cells with high regenerative capacity may not require this level of regulation, as new cells will bypass the need for long-term survival.
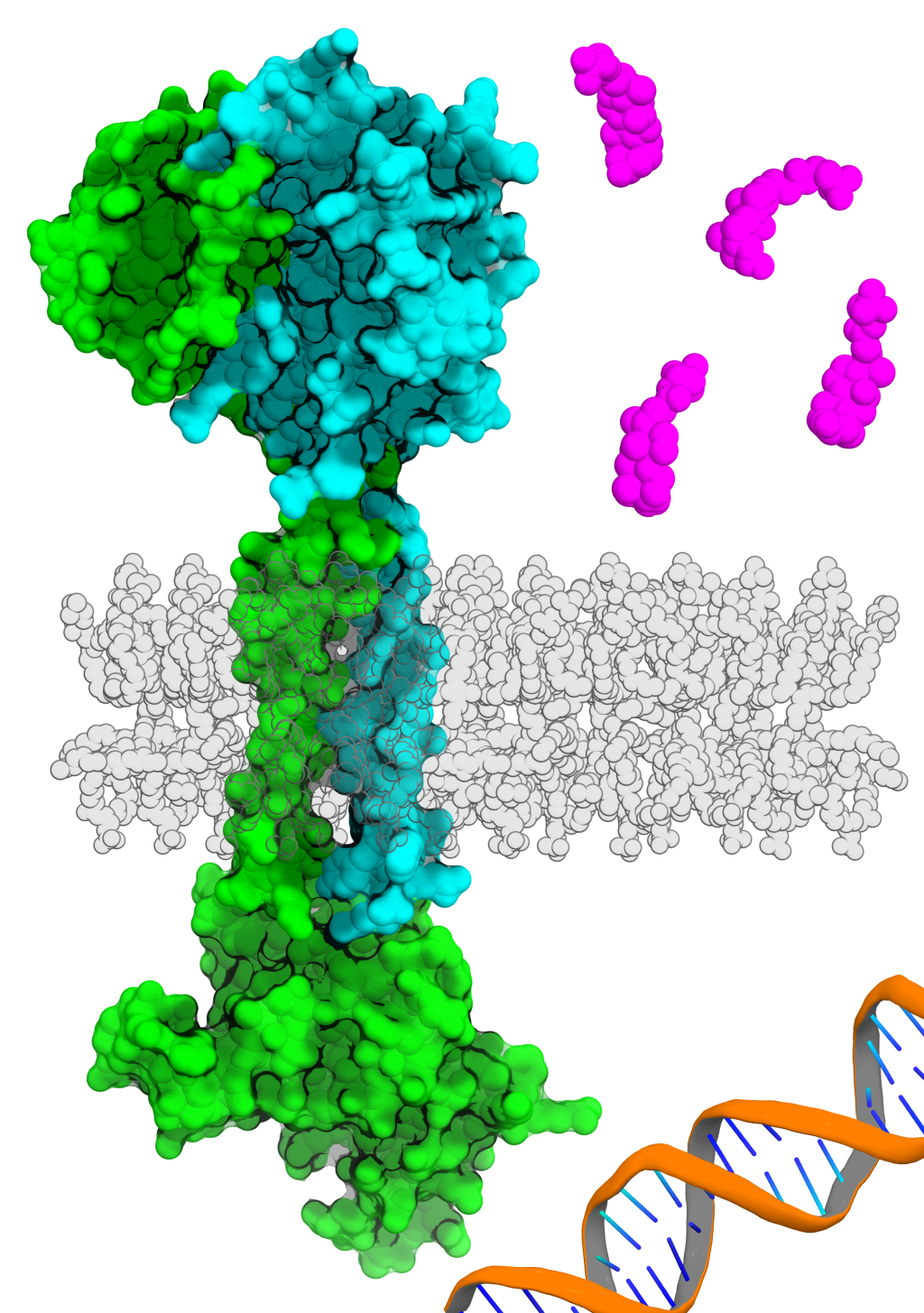
June 14, 2022
Co-component signal transduction systems: Fast-evolving virulence regulation cassettes discovered in enteric bacteria
Lisa N. Kinch, Qian Cong, Jananee Jaishankar, and Kim Orth
Description
We identified co-component signal transduction systems in enteric bacteria that are distantly related to the periplasmic bile acid receptor VtrA/VtrC from Vibrio parahaemolyticus. The newly identified co-component systems, which include the ToxR/ToxS master regulator of virulence, were identified using domain and operon organization combined with newly developed machine learning methods for structure prediction. The lipocalin-like fold adopted by all VtrC-like components suggests a regulatory role for sensing lipids in the virulence of enteric bacteria.
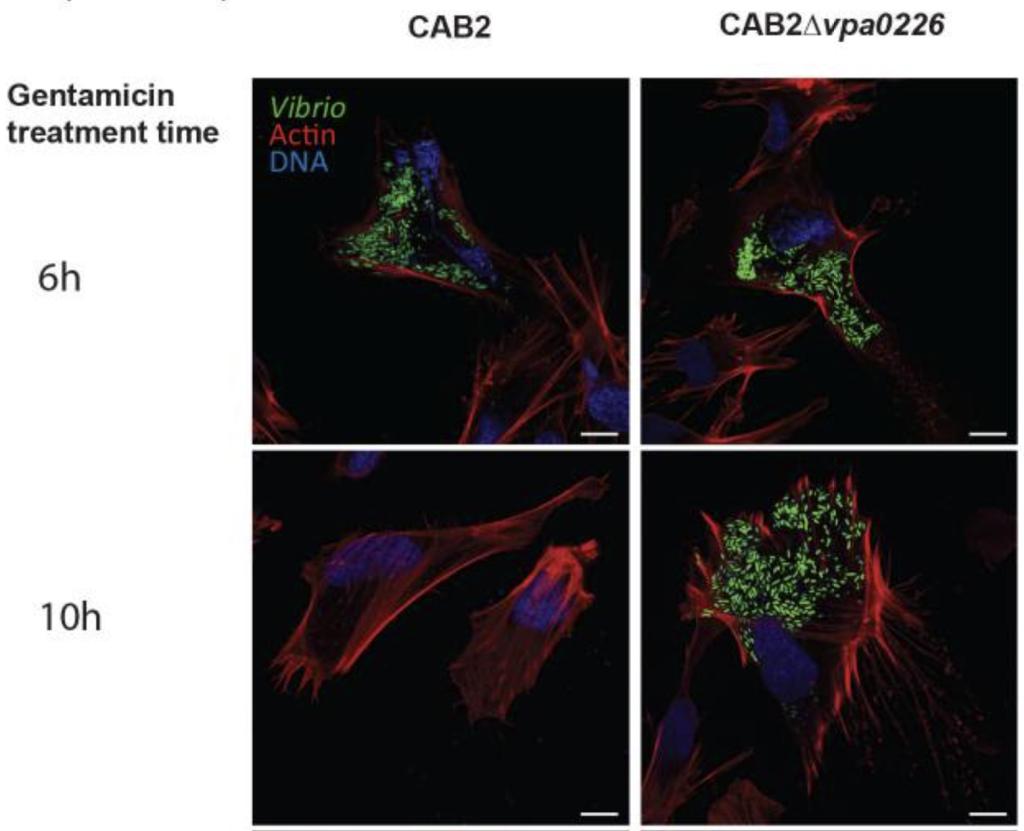
August 18, 2020
Vibrio deploys type 2 secreted lipase to esterify cholesterol with host fatty acids and mediate cell egress.
Suneeta Chimalapati, Marcela de Souza Santos, Alexander E Lafrance, Ann Ray, Wan-Ru Lee, Giomar Rivera-Cancel, Gonçalo Vale, Krzysztof Pawlowski, Matthew A Mitsche, Jeffrey G McDonald, Jen Liou, Kim Orth
Description
Using a combination of molecular tools, we found that VPA0226, a constitutively secreted lipase, is required for escape of V. parahaemolyticus from the host cells. This lipase must be delivered into the host cytoplasm where it preferentially uses fatty acids associated with innate immune response to esterify cholesterol. The activity weakens the plasma membrane and allows egress of the bacteria.
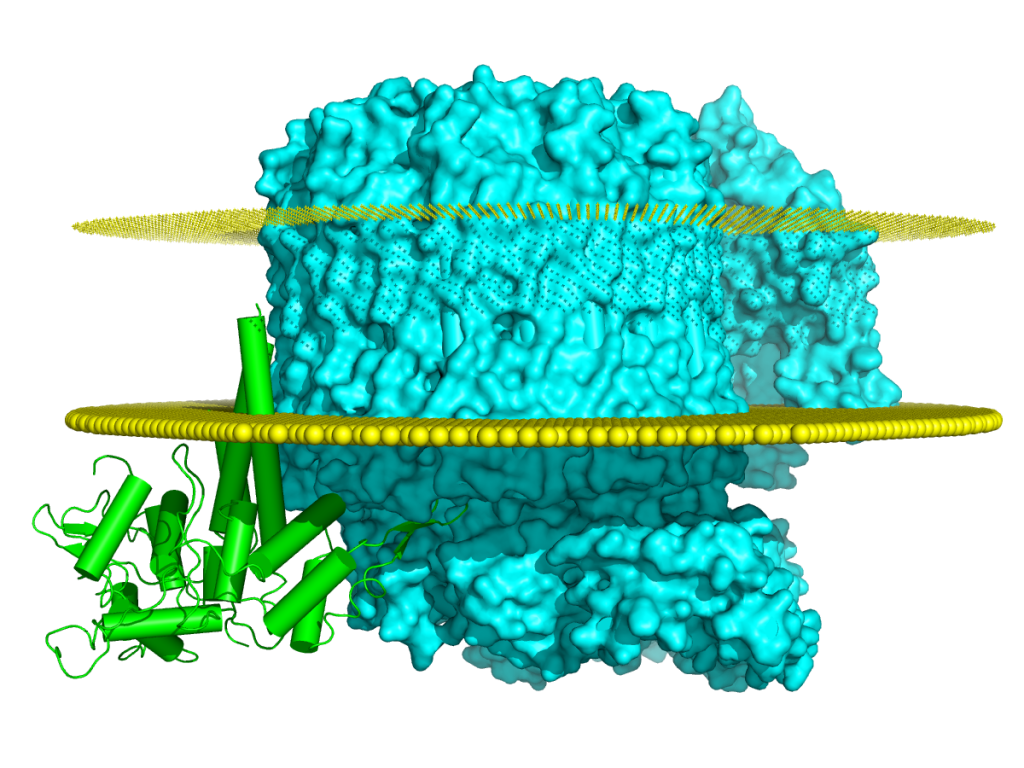
May 18, 2020
A distinct inhibitory mechanism of the V-ATPase by Vibrio VopQ revealed by cryo-EM.
Wei Peng, Amanda K Casey, Jessie Fernandez, Emily M Carpinone, Kelly A Servage, Zhe Chen, Yang Li, Diana R Tomchick, Vincent J Starai, Kim Orth
Description
The Vibrio parahaemolyticus T3SS effector VopQ targets host-cell V-ATPase, resulting in blockage of autophagic flux and neutralization of acidic compartments. Here, we report the cryo-EM structure of VopQ bound to the Vo subcomplex of the V-ATPase.
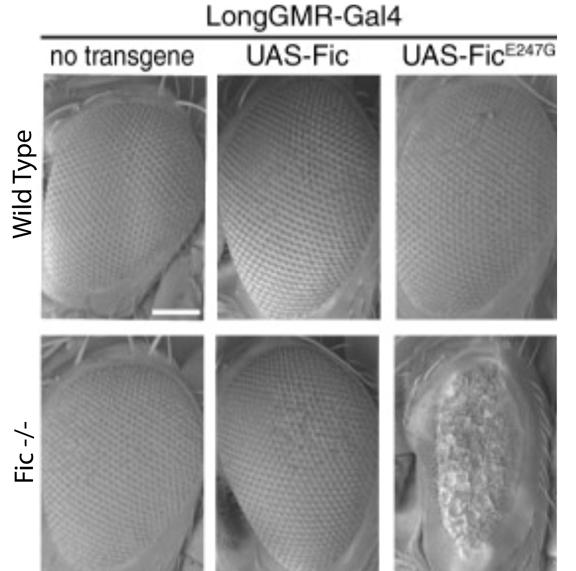
December 22, 2017
Fic-mediated deAMPylation is not dependent on homodimerization and rescues toxic AMPylation in flies.
Amanda K Casey, Andrew T Moehlman, Junmei Zhang, Kelly A Servage, Helmut Krämer, Kim Orth
Description
We show that excessive AMPylation by a constitutively active FicE247G mutant is lethal in Drosophila. This lethality is cell-autonomous, as directed expression of the mutant FicE247G to the fly eye does not kill the fly but rather results in a rough and reduced eye. Lethality and eye phenotypes are rescued by the deAMPylation activity of wild-type Fic.
July 5, 2016
Bile salt receptor complex activates a pathogenic type III secretion system
Peng Li, Giomar Rivera-Cancel, Lisa N Kinch, Dor Salomon, Diana R Tomchick, Nick V Grishin, Kim Orth
Description
We report the crystal structure of the periplasmic domains of the VtrA/VtrC heterodimer. The VtrC fold adopts a β-barrel with a hydrophobic inner chamber. We present biophysical and mutational analysis to demonstrate the hydrophobic chamber binds bile salts and activates the T3SS2 virulence network.
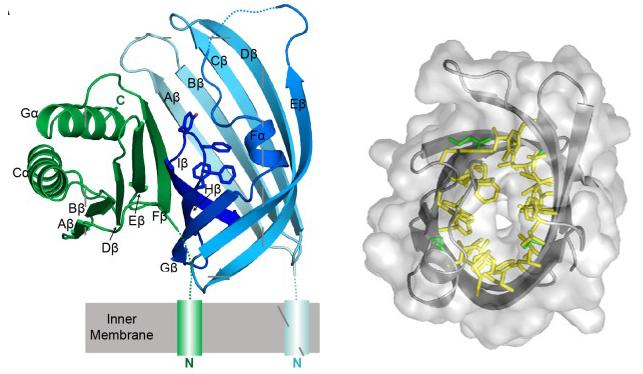
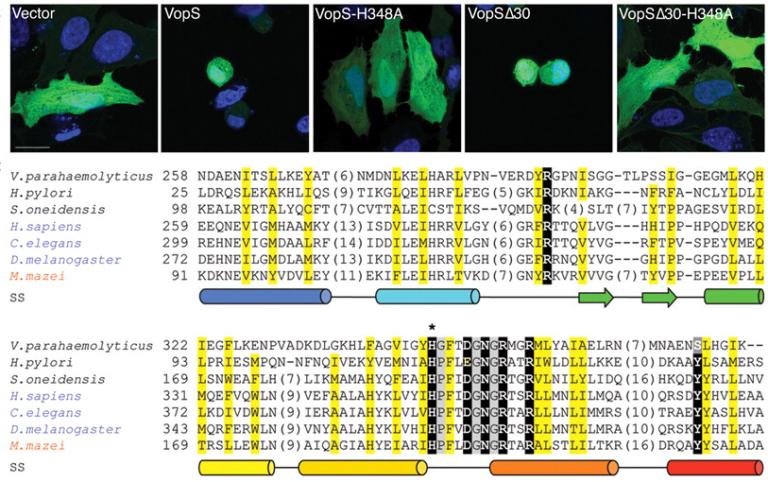
January 9, 2009
AMPylation of Rho GTPases by Vibrio VopS disrupts effector binding and downstream signaling
Melanie L Yarbrough, Yan Li, Lisa N Kinch, Nick V Grishin, Haydn L Ball, Kim Orth
Description
We found the Vibrio parahaemolyticus type III effector VopS Fic domain covalently modifies a conserved threonine residue on Rho, Rac, and Cdc42 GTPases with adenosine 5′-monophosphate (AMP). The resulting AMPylation prevented the interaction of Rho GTPases with downstream effectors to inhibit actin assembly in the infected cell. This discovery expanded the repertoire of posttranslational modifications for molecular signaling and established a paradigm for catalysis by Fic domains.
Publications by Year
2026
- Blevins AM, Peng W, Kinch LN, Monshad Z, Paredes AG, Volz C, Rutter J, Casey AK, Hicks KG, Orth K. Inhibition of FicD-mediated AMPylation and deAMPylation by Isoprenoid Diphosphates.
2025
- Jaishankar J, Yang H, O'Keefe IP, Tenaglia BM, Kinch LN, Ernst RK, Orth K. A critical role for Vibrio parahaemolyticus LPS to mediate evasion of host immune response during infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Aug 19;122(33):e2426547122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2426547122.
- Kim J, Zhang J, Kinch L, Shen J, Field S, Khan S, Klapproth JM, Forsberg KJ, Harris-Tryon T, Orth K, Cong Q, Ni J. Genetic and Microbial Analysis of Invasiveness for Escherichia coli Strains Associated With Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025;19(4):101451. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2024.101451.
- Casey AK, Stewart NM, Zaidi N, Gray HF, Fields HA, Sakurai M, Pinzon-Arteaga CA, Evers BM, Wu J, Orth K. Pre-clinical model of dysregulated FicD AMPylation causes diabetes by disrupting pancreatic endocrine homeostasis. Mol Metab. 2025 May;95:102120. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2025.
2024
- Peng W, Orth K. A small microcin plays a big role in V. cholerae interbacterial competition. Cell Host Microbe. 2024 Nov 13;32(11):1880-1881. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2024.10.011.
- Casey AK, Stewart NM, Zaidi N, Gray HF, Cox A, Fields HA, Orth K. FicD regulates adaptation to the unfolded protein response in the murine liver. Biochimie. 2024 Oct;225:114-124.
- Gulen B, Blevins A, Kinch LN, Servage KA, Stewart NM, Gray HF, Casey AK, Orth K. FicD sensitizes cellular response to glucose fluctuations in mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Sep 17;121(38):e2400781121.
- Peng W, Garcia N, Servage KA, Kohler JJ, Ready JM, Tomchick DR, Fernandez J, Orth K. Pseudomonas effector AvrB is a glycosyltransferase that rhamnosylates plant guardee protein RIN4. Sci Adv. 2024 Feb 16;10(7):eadd5108.
2023
- Kinch LN, Schaeffer RD, Zhang J, Cong Q, Orth K, Grishin N. Insights into virulence: structure classification of the Vibrio parahaemolyticus RIMD mobilome. mSystems. 2023 Dec 21;8(6).
- Humphreys JM, Teixeira LR, Akella R, He H, Kannangara AR, Sekulski K, Pleinis J, Liwocha J, Jiou J, Servage KA, Orth K, Joachimiak L, Rizo J, Cobb MH, Brautigam CA, Rodan AR, Goldsmith EJ. Hydrostatic Pressure Sensing by WNK kinases. Mol Biol Cell. 2023 Oct 1;34(11):ar109.
- Zou AJ, Kinch L, Chimalapati S, Garcia N, Tomchick DR, Orth K. Molecular determinants for differential activation of the bile acid receptor from the pathogen Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Biol Chem. 2023 Apr;299(4):104591.
- Gulen B, Casey A, Orth K. AMPylation of small GTPases by Fic enzymes. FEBS Lett. 2023 Mar;597(6):883-891.
- Kaval KG, Chimalapati S, Siegel SD, Garcia N, Jaishankar J, Dalia AB, Orth K. Membrane-localized expression, production and assembly of Vibrio parahaemolyticus T3SS2 provides evidence for transertion. Nat Commun. 2023 Mar 2;14(1):1178.
2022
- Lafrance AE, Chimalapati S, Garcia Rodriguez N, Kinch LN, Kaval KG, Orth K. Enzymatic Specificity of Conserved Rho GTPase Deamidases Promotes Invasion of Vibrio parahaemolyticus at the Expense of Infection. mBio. 2022 Aug 30;13(4):e0162922.
- Casey AK, Gray HF, Chimalapati S, Hernandez G, Moehlman AT, Stewart N, Fields HA, Gulen B, Servage KA, Stefanius K, Blevins A, Evers BM, Krämer H, Orth K. Fic-mediated AMPylation tempers the unfolded protein response during physiological stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Aug 9;119(32):e2208317119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2208317119.
- Kinch LN, Cong Q, Jaishankar J, Orth K. Co-component signal transduction systems: Fast-evolving virulence regulation cassettes discovered in enteric bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Jun 14;119(24):e2203176119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2203176119.
2021
- Ebrahimzadeh T, Kuprasertkul A, Neugent ML, Lutz KC, Fuentes JL, Gadhvi J, Khan F, Zhang C, Sharon BM, Orth K, Li Q, Zimmern PE, De Nisco NJ. Urinary prostaglandin E2 as a biomarker for recurrent UTI in postmenopausal women. Life Sci Alliance. 2021 May 6;4(7):e202000948. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202000948.
- De Nisco, N. J., Casey, A. K., Kanchwala, M., Lafrance, A. E., Coskun, F. S., Kinch, L. N., . . . & Orth, K. (2021). Manipulation of ire1-dependent mapk signaling by a vibrio agonist-antagonist effector pair. MSystems, 6(1). doi:10.1128/msystems.00872-20
- Fernandez, J., Lopez, V., Kinch, L., Pfeifer, M. A., Gray, H., Garcia, N., . . . & Orth, K. (2021). Role of two metacaspases in development and pathogenicity of the Rice Blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. MBio, 12(1). doi:10.1128/mbio.03471-20
- Stefanius, K., Servage, K., & Orth, K. (2021). Exosomes in cancer development. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development, 66, 83-92. doi:10.1016/j.gde.2020.12.018
2020
- Chimalapati, S., de Souza Santos, M.*, Lafrance, A., Ray, A., Lee, W-R., Rivera-Cancel, G., Vale, G., Pawłowski, K., Mitsche, M., McDonald, J.G. , Liou, J. & Orth, K. Vibrio deploys a Type 2 secreted lipase to esterify cholesterol with host fatty acids and mediate T3SS2-mediated cell egress. eLife, 9:e58057.
- Peng, W., Fernandez, J., Casey, A. K., Kinch, L. N., Tomchick, D. R., & Orth, K. (2020). Structures of an intact yeast v-atpase alone and in complex with bacterial effector vopq. doi:10.1101/2020.07.16.207225
- Peng, W., Casey, A. K., Fernandez, J., Carpinone, E. M., Servage, K. A., Chen, Z., Li, Y., Tomchick, D. R., Starai, V. J., & Orth, K. (2020). A distinct inhibitory mechanism of the V-ATPase by Vibrio VopQ revealed by cryo-EM. Nature structural & molecular biology, 10.1038/s41594-020-0429-1. Advance online publication.
- Servage, K. A., Stefanius, K., Gray, H. F., & Orth, K. (2020). Proteomic Profiling of Small Extracellular Vesicles Secreted by Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells Implicated in Cellular Transformation. Scientific reports, 10(1), 7713.
2019
- Yang, H.*, de Souza Santos, M.*, Lee, J., Law, H.T., Chimalapati, S., Verdu, E.F., Orth, K. #, and Vallance, B.A.# A novel mouse model of enteric Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection reveals the T3SS2effector VopC plays a key role in tissue invasion and gastroenteritis. (2019) *contributed equally, #co-corresponding. mBio 17;10(6). pii: e02608-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02608-19.
- Stefanius, K., Servage, K., de Souza Santos, M., Chimalapati, S., Gray, H., Kim, M., Brekken, R. & Orth, K. Pancreatic Cancer Cell Exosomes Initiate Cellular Transformation and Tumor formation. eLife, (2018) May 28;8. pii: e40226. doi: 10.7554/eLife.40226.
- Peng, W., de Souza Santos, M., Tomchick, D. & Orth, K. Assembly mechanism of the E. coli hemolysin ClyA pore complexes. PLoS ONE (2019) May 2;14(5):e0213423. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0213423.
- De Nisco, N., Neugent, M., Mull, J., Chen, L., Kuprasertkul, A., de Souza Santos, M., Palmer, K., Zimmern, P. & Orth, K. Direct detection of tissue-resident bacteria and chronic inflammation in the bladder wall of postmenopausal women with recurrent urinary tract infection. Journal of Molecular Biology (2019) Apr 17. pii: S0022-2836(19)30202-5.
2018
- Sreelatha, A., Yee, S.S., Lopez, V.A., Park, B.C., Kinch, L., Pilch, S., Servage, K.A., Zhang, J., Jiou, J., Karasiewicz, M., M?obocka, M., Grishin, N., Orth, K, Kucharczyk, R., Paw?owski, K., Tomchick, D. R., and Tagliabracci. V.S. Protein AMPylation by an evolutionarily conserved pseudokinase. Cell. (2018) 175(3):809-821
- Moehlman, A.T., Casey, A.K., Servage, K., Orth, K* & Krämer, H.* Regulation of the Unfolded Protein Response by BiP AMPylation protects photoreceptors from light-dependent degeneration. eLife. (2018) Jul 17:7. Pii:e38752. doi:10.7554/eLife.38752. PMID: 30015618.
- Orth, K. My winding trail while fulfilling my love for science and family. J Biol Chem.. (2018) pii: jbc.AW118.003225. doi: 10.1074/jbc.AW118.003225
- Chimalapati,S., de Souza Santos, M., Servage, K., De Nisco, N.J., Dalia, A.B. & Orth, K. Natural transformation of Vibrio parahaemolyticus: A rapid method to create genetic deletions. J. Bac. 2018 Jul 10;200(15). pii: e00032-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00032-18
- Fernandez, J. & Orth, K. Rise of a Cereal Killer: The Biology of Magnaporthe oryzae Biotrophic Growth. Trends in Microbiology (2018)
- De Nisco, N.J., Rivera-Cancel, G. & Orth, K. The biochemistry of sensing: How enteric pathogens regulate type III secretion in response to environmental and host cues. mBio. (2018) vol. 9 no. 1 e02122-17
2017
- Ray, A., Schwartz, N., de Souza Santos, M., Zhang, J. Orth, K & Salomon, D. Type VI secretion system MIX-effectors are targeting at both Bacterial and eukaryotic neighbors. EMBO Report. (2017) e201744226
- Casey, A.K. & Orth, K. Enzymes involved in AMPylation and deAMPylation. Chemical Reviews. (2017) Aug 18. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00145.
- Cancel-Rivera, G. & Orth, K. Biochemical basis for activation of virulence genes by bile salts in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Gut Microbes.. (2017) Jan 27:0. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2017.1287655
- Casey, A.K., Moelman, A., Zhang, J., Servage, K., Kramer, H. & Orth, K. Fic-mediated deAMPylation of BiP is not dependent on homo-dimerization and rescues toxic AMPylation in flies. J Biol Chem. (2017) 292 (51) pg 21193-21204)
- de Souza Santos, M., Salomon, D. & Orth, K. T3SS effector VopL inhibits the host ROS response, promoting the intracellular survival of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. PLoS Pathog (2017) 13(6): e1006438. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.100643
- Li,P., Salomon, D., Kinch, L.N., Ray, A., Dalia, A.B., Cong, Q., Ninan, L., Camilli, A., Grishin, N.V. & Orth, K. Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease (AHPND) causing Vibrio parahaemolyticus contains a virulent Type VI Secretion System (T6SS) with anti-bacterial activities. Appl Environ Microbiol. (2017) Apr 21. pii: AEM.00737-17. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00737-17
- De Nisco, N.J., Kanchwala, M., Li, P., Fernandez, J., Xing, C. & Orth, K. Cytotoxic Vibrio T3SS1 Rewires Host Gene Expression to Subvert Cell Death Signaling and Activate Cell Survival Networks. Sci Signal (2017) May 16;10(479). pii: eaal4501. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aal4501
- De Nisco, N.J., Orth, K. & VanHook, A.M., Signaling Science Podcast: Vibrio Rewires host cells. Sci Signal. 2017 May 16;10(479). pii: eaan5621. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aan5621
2016
- Huebinger, R.M., Stones, D.H., de Souza Santos, M., Carlson, D.L., Song, J., Vaz, D.P., Keen, E., Wolf, S.E., Orth, K. & Krachler, A. M. Targeting bacterial adherence inhibits multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection following burn injury. (2016) Scientific Reports Dec 20;6:39341. doi: 10.1038/srep39341
- Li, P., Rivera-Cancel, G., Kinch, L.N., Salomon, D., Tomchick, D.R., Grishin, N.V. & Orth, K. Bile Salt Receptor Complex Activates a Pathogenic Type III Secretion System (2016) eLife 5:e15718.
- Ray, A., Kinch, L.N., , de Souza Santos, M., Grishin, N.V., Orth, K. & Salomon, D. Proteomics analysis reveals previously uncharacterized virulence factors in Vibrio proteolyticus (2016) mBio 7(4):e01077-16. doi:10.1128/mBio.01077-16.
2015
- Salomon, D., Klimko, J.A., Trudgian, D.C., Kinch, L.N., Grishin, N.V., Mirzaei, H & Orth, K. Type VI secretion system toxins horizontally shared between marine bacteria (2015) PLoS Pathogen Aug 25;11(8):e1005128. PMID 26305100.
- Sreelatha, A., Bennett, T.L., Carpinone, E.M., O’Brien, K.M., Jordan, K.D., Burdette, D.L., Orth, K, & Starai, V.J. The Vibrio effector protein, VopQ, inhibits fusion of V-ATPase containing membranes. (2015) PNAS 112(1):100-5 PMID:25453092.
2014
- Ham H., Woolery A.R., Tracy C., Stenesen D., Krämer H. & Orth, K. Unfolded protein response-regulated dFic reversibly AMPylates BiP during ER homeostasis. (2014) JBC 289(52):36059-69 PMID: 25395623.
- Calder, T., Santos, M.S., Attah, V., Klimko, J., Frernandez, J., Salomon, D., Krachler, A.M., & Orth, K. Structural and regulatory mutations in Vibrio parahaemolyticus type III secretion systems display variable effects on virulence. (2014) FEMS 361(2):107-14. PMID 25288215.
- Woolery, A.R., Yu, X., LaBaer, J.& Orth, K. AMPylation of Rho GTPases subverts multiple host signaling processes. (2014) JBC 289(47):32977-88. PMID 25301945.
- de Souza Santos, M.S.. & Orth, K. Intracellular Vibrio parahaemolyticus Escapes the Vacuole and Establishes a Replicative Niche in the Cytosol of Epithelial Cells. (2014) mBio 9;5(5):e01506-14.
- Yu, X., Woolery, A.R., Luong, P., Hao, Y.H., Grammel, M., Westcott, N., Park, J., Wang, J., Bian, X., Demirkan, G., Hang, H.C., Orth, K. & LaBaer, J. Click chemistry-based detection of global pathogen-host AMPylation on self-assembled human protein microarrays. (2014) Mol & Cell Proteomics 13(11):3164-76. PMID 25073739.
- Calder, T., Kinch, L.N., Fernandez, J., Salomon, D., Grishin, N.V., & Orth, K. Vibrio type III effector VPA1380 is related to the cysteine protease domain of large bacterial toxin PLoS ONE 6;9(8):e104387 PMID 25099122.
- Salomon, D., Klimko, & Orth, K. H-NS regulates the Vibrio parahaemolyticus type VI secretion system 1. (2014) Microbiology 160(Pt9):1867-73. PMID:24987102.
- Salomon, D., Kinch, L.N., Trudgian, D.C., Guo, X., Klimko, J.A., Grishin, N.V., Mirzaei, H & Orth, K. Marker for type VI secretion system effectors. PNAS USA (2014) 111(25):9271-6 PMID 24927539.
- Lewallen,D.M., Sreelatha, A., Dharmarajan, V., Madoux, F., Chase,, F. ,Griffin, P.R., Orth, K., Hoddler, P. & Thompson, P.R. Inhibiting AMPylation: a novel screen to identify the first small molecule inhibitors of protein AMPylation. ACS Chem Biol (2014) 9(2): 433-432 PMC3944102.
2013
- Sreelatha, A., Orth, K., & Starai, V.J. The pore-forming bacterial effector, VopQ, halts autophagic turnover. Autophagy (2013) 9(12): 2169-70. PMID:24145145.
- Salomon D., Guo, Y., Kinch, L.N., Grishin, N.V., Mirzaei, H. & Orth, K. Effectors of animal and plant pathogens use a common domain to bind host phosphoinositides. Nature Communications (2013) 4:2973. Doi:10.1038/n,comms3973.
- Hawley, C.A., Watson, C., Orth, K. & Krachler, A-M. High-affinity binding of bacterial fibronectin-binding proteins to host cells inhibits critical steps in wound healing. PloS ONE (2013) 8.11:e81216.
- Sreelatha, A., Bennett,T. L., Zheng, H., Jiang, Q.X., Orth, K.*, & Starai, V.J.* Vibrio VopQ forms a gated outward rectifying channel that disrupts host ion homeostasis. PNAS USA (2013) 110(28):11559-64.
- Altura, M.A., Heath-Heckman, E.A., Gillette, A. Kremer, A-M, Krachler, A.M. Brennean, c., Ruby, E.G., Orth, K., McFall-Ngai, M.J. (2013) The first engagement of partners in the Euprymna scolopes-Vibrio fischeri symbiosis is a two-step process initiated by a few environmental symbiont cells. Environ Microbiol. (2013) Jun 11. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.12179 (Epub ahead of print).
- Salomon, D. & Orth, K. What Pathogens Have Taught Us About Posttranslational Modifications (2013) Cell Host Pathogens 14:3 269-279.
- Krachler, A-M. & Orth, K. Made to stick: Anti-adhesion therapy for bacterial infections as an alternative to conventional antimicrobials. (2013) Microbe 8:286-290.
- Krachler, A-M. & Orth, K. Targeting the bacteria-host interface: strategies in anti-adhesion therapy (2013) Virulence 4(4): 284-94.
- Salomon, D. & Orth, K. Lost after translation: post-translational modifications by bacterial type III effectors. (2013) Current Opinions in Microbiology 6(2):213-20.
- Zhang, L.L & Orth, K. Virulence Determinants for Vibrio parahaemolyticus Infection. Current Opinions in Microbiology (2013) 16(1):70-7.
- Salomon, D., Gonzalez, H., Updegraff, B.L. & Orth, K. Vibrio parahaemolyticus Type VI Secretion System 1 is Activated in Marine Conditions to Target Bacteria, and is Differentially Regulated from System 2. PLoS ONE (2013) 8:4 e61086.
2012
- Ham, H. & Orth, K. The Role of Type III Secretion System 2 in Vibrio parahaemolyticus Pathogenicity. J Microbiol. (2012) Oct;50(5):719-25. PMID:23124738[PubMed - in process]
- Krachler AM & Orth, K. In vitro characterization of Multivalent Adhesion Molecule 7-based inhibition of multidrug-resistant bacteria isolated from wounded military personnel. Virulence (2012) (In Press)
- Alto, N.M. & Orth, K. Subversion of cell signaling by pathogens. In Signal Transduction Textbook. Cold Spring Harbor Press (2012).
- Zhang, L.L, Krachler, A-M, Broberg, CA, Li, Y, Mirzaei, H, Gilpin, CJ & Orth, K. Type III effector VopC mediates invasion for Vibrio species. Cell Reports (2012) 1(5): 453-460.
- Rahman, M., Ham, H., Liu, X., Sugiura, Y., Orth, K. and Krämer, H. Visual neurotransmission in Drosophila requires expression of dFic in glial capitate projections. Nature Neuroscience (2012) Apr 29. doi: 10.1038/nn.3102. [Epub ahead of print] PMID:22544313.
- Krachler, A-M, Ham, H. & Orth, K. Turnabout is fair play: Use of the bacterial Multivalent Adhesion Molecule 7 as an antimicrobial agent. Virulence (2012) 1;3(1).
2011
- Krachler AM & Orth, K. Functional characterization of the interaction between bacterial adhesin multivalent adhesion molecule 7 (MAM7) protein and its host cell ligands. J Biol Chem. (2011) Nov 11;286(45):38939-47.
- Grammel M, Luong P, Orth, K, Hang HC. A chemical reporter for protein AMPylation. J Am Chem Soc. (2011) Nov 2;133(43):17103-5.
- Krachler, A-M, Woolery, A.R. & Orth, K. Host-pathogen interactions: Manipulation of kinase signaling by bacterial pathogens. (2011) J. Cell Biol 195(7):1083-92.
- Krachler AM, Ham H, Orth, K. The outer membrane adhesion factor MAM7 initiates host cell binding during infection with Gram-negative pathogens. (2011) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. Epub June 2011.
- Ham H., Sreelatha, A. & Orth, K. (2011) Manipulation of Host Membranes by Bacterial Effectors. Nature Reviews Microbiology 9(9):635-46.
- Broberg, CA, Calder, TJ, & Orth, K. Vibrio parahaemolyticus cell biology and pathogenicity determinants. Microbes Infect. 2011 Nov;13(12-13):992-1001. Epub 2011 Jul 7.
- Hao YH, Chuang T, Ball HL, Luong P, Li Y, Flores-Saaib RD, Orth, K. Characterization of a rabbit polyclonal antibody against threonine-AMPylation. (2011) J Biotechnol. 151(3):251-4.
- Li Y, Al-Eryani R, Yerbrough ML, Orth, K, Ball HL. Characterization of AMPylation on threonine, serine, and tyrosine using mass spectrometry. (2011) J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 22(4):752-61.
- Krachler AM, Orth, K. Black Spot, Black Death, Black Pearl: Tales of Bacterial Effectors. Chapter in Avancées et nouvelles technologies en Toxinologie – Advances and new technologies in Toxinology (SFET, ed.). ISSN 1760 – 6004.
2010
- Broberg CA, Zhang L, Gonzalez H, Laskowski-Arce MA, Orth, K. A Vibrio effector protein is an inositol phosphatase and disrupts host cell membrane integrity. (2010) Science. 329(5999):1660-2.
- Luong P, Kinch LN, Brautigam CA, Grishin NV, Tomchick DR, Orth, K. Kinetic and structural insights into the mechanism of AMPylation by VopS Fic domain. (2010) J Biol Chem. 285(26):20155-63.
- Broberg CA, Orth, K. Tipping the balance by manipulating post-translational modifications. (2010) Curr Opin Microbiol. 13(1):34-40.
- Woolery AR, Luong P, Broberg CA, Orth, K. AMPylation: Something Old is New Again. (2010) Front Microbiol. 1:113.
2009
- Burdette DL, Seemann J, Orth, K. Vibrio VopQ induces PI3-kinase-independent autophagy and antagonizes phagocytosis. (2009) Mol Microbiol. 73(4):639-49.
- Kinch LN, Yarbrough ML, Orth, K, Grishin NV. Fido, a novel AMPylation domain common to fic, doc, and AvrB. (2009) PLoS One. 4(6):e5818.
- Yarbrough ML, Orth, K. AMPylation is a new post-translational modification. (2009) Nat Chem Biol. 5(6):378-9.
- Yarbrough ML, Li Y, Kinch LN, Grishin NV, Ball HL, Orth, K. AMPylation of Rho GTPases by Vibrio VopS disrupts effector binding and downstream signaling. (2009) Science. 323(5911):269-72.
- Burdette DL, Yarbrough ML, Orth, K. Not without a cause: Vibrio parahaemolyticus induces acute autophagy and cell death. (2009) Autophagy. 5(1):100-2.
2008
- Mukherjee S, Orth, K. Microbiology. A protein pupylation paradigm. (2008) Science. 322(5904):1062-3.
- Laskowski-Arce MA, Orth, K. Acanthamoeba castellanii promotes the survival of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. (2008) Appl Environ Microbiol. 74(23):7183-8.
- Burdette L, Yarbrough ML, Orvedahl A, Gilpin CJ, Orth, K. Vibrio parahaemolyticus orchestrates a multifaceted host cell infection by induction of autophagy, cell rounding, and then cell lysis. (2008) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105(34):12497-502.
- Mukherjee S, Orth, K. in vitro signaling by MAPK and NFkappaB pathways inhibited by Yersinia YopJ. (2008) Methods Enzymol. 438:343-53.
- Le Negrate G, Faustin B, Welsh K, Loeffler M, Krajewska M, Hasegawa P, Mukherjee S, Orth, K, Krajewski S, Godzik A, Guiney DG, Reed JC. Salmonella secreted factor L deubiquitinase of Salmonella typhimurium inhibits NF-kappaB, suppresses IkappaBalpha ubiquitination and modulates innate immune responses. (2008) J Immunol. 180(7):5045-56.
- Mukherjee S, Negi VS, Keitany G, Tanaka Y, Orth, K. In vitro activation of the IkappaB kinase complex by human T-cell leukemia virus type-1 Tax. (2008) J Biol Chem. 283(22):15127-33.
- Hao YH, Wang Y, Burdette D, Mukherjee S, Keitany G, Goldsmith E, Orth, K. Structura requirements for Yersinia YopJ inhibition of MAP kinase pathways. (2008) PLoS One. 3(1):e1375.
- Trosky JE, Liverman AD, Orth, K. Yersinia outer proteins: Yops. (2008) Cell Microbiol. 10(3):557-65.