 Delineation of the post-prostatectomy clinical target volume using deep learning for prostate cancer radiotherapy
Delineation of the post-prostatectomy clinical target volume using deep learning for prostate cancer radiotherapy Organ Segmentation and Treatment Target Delineation
Accurate delineation of tumors and sensitive structures is important for many medical applications. One example is treatment planning in cancer radiotherapy. Although many auto-segmentation algorithms have been developed and implemented in clinical practice, none of them are satisfactory and manual contouring is often required. Such failure is mainly because conventional segmentation methods are purely based on local information in the images. Especially for treatment target delineation we often rely on information beyond the images which is very challenging, if not impossible, for conventional methods. We have been investigating deep learning based strategies to solve this problem.
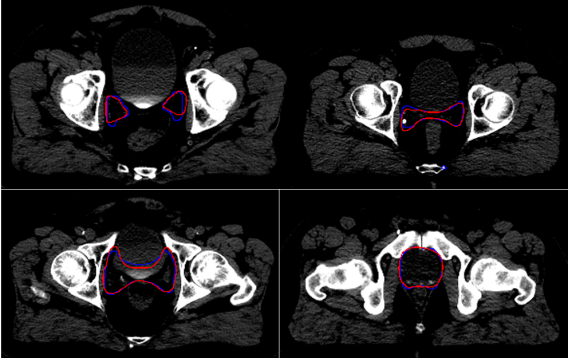
The figure below shows an example of delineating the post-prostatectomy clinical target volume using deep learning for prostate cancer radiotherapy, where in addition to CT images, we need to use information like surgery reports, surgical pathology, pre-operative MRI knowledge of tumor location and organ invasion, etc.
Publications
- Liang X, Morgan H, Bai T, Dohopolski M, Nguyen D, Jiang S. (2023) Deep learning based direct segmentation assisted by deformable image registration for cone-beam CT based auto-segmentation for adaptive radiotherapy. Phys Med Biol. (journal)
- Balagopal A, Nguyen D, Bai T, Dohopolski M, Lin MH, Jiang S. (2023) Prior guided deep difference meta-learner for fast adaptation to stylized segmentation. (arXiv preprint)
Image Reconstruction and Restoration
By introduction of machine learning and data-driven methods, a paradigm shift has happened in the field of imaging in general and accordingly these new methods have a high translational impact in the area of medical imaging.
These impacts are not limited to only image analysis and pattern recognition techniques but also they are used widely in the field of image reconstruction. Recently, multiple groups worldwide, with encouraging results and increasing interest, are actively exploring deep learning techniques for image reconstruction and other inverse problems.
Currently, our team is working on developing new machine learning based methods for implementing MRI-only planning into the clinic. Challenges include producing robust MRI-only patient models and synthetic CT scans with accurate geometry and electron densities.
However, our novel machine learning based method allows us to simultaneously achieve electron density map for dose calculation and automatic segmentation of the target and OAR.
The successful completion of this research will provide essential tools to establish effective MRI-based RT planning in routine clinical practice, which will improve normal and target tissue delineation and localization for more accurate radiation delivery.
Publications
- Liang X, Yen A, Bai T, Godley A, Shen C, Wu J, Meng B, Lin MH, Medin P, Yan Y, Owrangi A, Desai N, Hannan R, Garant A, Jiang S, Deng J. (2023) Bony structure enhanced synthetic CT generation using Dixon sequences for pelvis MR‐only radiotherapy. Med Phys. (journal)
- Bai T, Wang B, Nguyen D, Jiang S. (2021) Deep dose plugin: Towards real-time Monte Carlo dose calculation through a deep learning-based denoising algorithm. Mach Learn: Sci Technol. (journal)